Android显示框架:WindowManagerService关于窗口的计算流程
前面的两篇文章:
我们分析了Activity应用视图的创建与渲染流程,主要针对的是View,下面我们来分析Window。Window是View的直接管理者。Window是一个抽象类,它的实现类是PhoneWindow,Window的管理通过WindowManager,WindowManager 是外界访问Window的入口,真正完成功能的是WindowManagerService,两者的通信一个IPC过程。
WindowManagerService是窗口的真正管理者,它管理者所有的窗口,如下所示:

Window其实是一个抽象概念,每一个Window都对应着一个View和ViewRootImpl,View与Window通过ViewRootImpl来建立联系,因此Window并不是实际存在的,它是以View的形式存在的。WindowManagerService 的主要作用就是计算Window的大小,层级以及创建、切换Window。
概括来说,WindowManagerService决定了Window在哪显示以及显示多大等问题。
- 每一个Activity窗口的大小都等于屏幕的大小,因此,只要对每一个Activity窗口设置一个不同的Z轴位置,然后就可以使得位于最上面的,即当前被激活的Activity窗口,才是可见的。
- 每一个子窗口的Z轴位置都比它的父窗口大,但是大小要比父窗口小,这时候Activity窗口及其所弹出的子窗口都可以同时显示出来。
- 对于非全屏Activity窗口来说,它会在屏幕的上方留出一块区域,用来显示状态栏。这块留出来的区域称对于屏幕来说,称为装饰区(decoration),而对于Activity窗口来说,称为内容边衬区(Content Inset)。
- 输入法窗口只有在需要的时候才会出现,它同样是出现在屏幕的装饰区或者说Activity窗口的内容边衬区的。
- 对于壁纸窗口,它出现需要壁纸的Activity窗口的下方,这时候要求Activity窗口是半透明的,这样就可以将它后面的壁纸窗口一同显示出来。
- 两个Activity窗口在切换过程,实际上就是前一个窗口显示退出动画而后一个窗口显示开始动画的过程,而在动画的显示过程,窗口的大小会有一个变化的过程,这样就导致前后两个Activity窗口的 大小不再都等于屏幕的大小,因而它们就有可能同时都处于可见的状态。事实上,Activity窗口的切换过程是相当复杂的,因为即将要显示的Activity窗口可能还会被设置一个启动窗口(Starting Window)。 一个被设置了启动窗口的Activity窗口要等到它的启动窗口显示了之后才可以显示出来。
这里提到了一个Z轴顺序的概念,即z-order。
z-order,手机屏幕是以左上角为原点,向右为X轴方向,向下为Y轴方向的一个二维空间。为了方便管理窗口的显示次序,手机的屏幕被扩展为了 一个三维的空间,即多定义了 一个Z轴,其方向为垂直于屏幕表面指向屏幕外。多个窗口依照其前后顺序排布在这个虚拟的Z轴上,因此 窗口的显示次序又被称为Z序(Z order)。
一 窗口大小的计算
窗口大小的计算序列图

我们来分析窗口大小(X轴、Y轴)的计算流程,在介绍窗口的计算流程之前,我们先来了解一下窗口的组成。
窗口有内容窗口(Content Region),内容边距(Content Inset)与可见边距(Visible Inset)组成,如下图:
content-left、content-right、content-top、content-bottom分别用来描述内容区域与窗口区域的左右上下边界距离。 visible-left、visible-right、visible-top、visible-bottom分别用来描述可见区域与窗口区域的左右上下边界距离。

关键点1:ViewRoot.performTraversals()
从前面的文章可知,Window大小的计算是从函数ViewRoot.performTraversals()开始,向WindowManagerService发送一个进程间通信请求,请求计算 Window窗口大小。
这个函数一共600多行代码,相对比较复杂,它主要用来计算窗口的大小。我们拆开一段段来看。
1.1 获取Activity当前宽度desiredWindowWidth与当前高度desiredWindowHeight
public final class ViewRoot extends Handler implements ViewParent,
View.AttachInfo.Callbacks {
}
private void performTraversals() {
//1 获取Activity当前宽度desiredWindowWidth与当前高度desiredWindowHeight
// cache mView since it is used so much below...
final View host = mView;
if (DBG) {
System.out.println("======================================");
System.out.println("performTraversals");
host.debug();
}
if (host == null || !mAdded)
return;
mTraversalScheduled = false;
mWillDrawSoon = true;
boolean windowResizesToFitContent = false;
boolean fullRedrawNeeded = mFullRedrawNeeded;
boolean newSurface = false;
boolean surfaceChanged = false;
WindowManager.LayoutParams lp = mWindowAttributes;
int desiredWindowWidth;
int desiredWindowHeight;
int childWidthMeasureSpec;
int childHeightMeasureSpec;
final View.AttachInfo attachInfo = mAttachInfo;
final int viewVisibility = getHostVisibility();
boolean viewVisibilityChanged = mViewVisibility != viewVisibility
|| mNewSurfaceNeeded;
float appScale = mAttachInfo.mApplicationScale;
WindowManager.LayoutParams params = null;
if (mWindowAttributesChanged) {
mWindowAttributesChanged = false;
surfaceChanged = true;
params = lp;
}
//mWinFrame用来保存Activity窗口的高度与宽度信息,注意该变量的高度和宽度可能会被WindowManagerService
//主动请求应用进程修改,修改后的值保存在mFrame中。
Rect frame = mWinFrame;
//mFirst为true则表示Activity窗口是第一次请求执行策略、布局与绘制操作,
if (mFirst) {
fullRedrawNeeded = true;
mLayoutRequested = true;
DisplayMetrics packageMetrics =
mView.getContext().getResources().getDisplayMetrics();
desiredWindowWidth = packageMetrics.widthPixels;
desiredWindowHeight = packageMetrics.heightPixels;
// For the very first time, tell the view hierarchy that it
// is attached to the window. Note that at this point the surface
// object is not initialized to its backing store, but soon it
// will be (assuming the window is visible).
attachInfo.mSurface = mSurface;
attachInfo.mUse32BitDrawingCache = PixelFormat.formatHasAlpha(lp.format) ||
lp.format == PixelFormat.RGBX_8888;
attachInfo.mHasWindowFocus = false;
attachInfo.mWindowVisibility = viewVisibility;
attachInfo.mRecomputeGlobalAttributes = false;
attachInfo.mKeepScreenOn = false;
viewVisibilityChanged = false;
mLastConfiguration.setTo(host.getResources().getConfiguration());
host.dispatchAttachedToWindow(attachInfo, 0);
//Log.i(TAG, "Screen on initialized: " + attachInfo.mKeepScreenOn);
} else {
desiredWindowWidth = frame.width();
desiredWindowHeight = frame.height();
if (desiredWindowWidth != mWidth || desiredWindowHeight != mHeight) {
if (DEBUG_ORIENTATION) Log.v(TAG,
"View " + host + " resized to: " + frame);
fullRedrawNeeded = true;
mLayoutRequested = true;
//当前宽高不等于上次计算的宽高,则说明窗口大小发生了变化,将windowResizesToFitContent置为true
windowResizesToFitContent = true;
}
}
...
}本小段函数主要用来获取Activity当前宽度desiredWindowWidth与当前高度desiredWindowHeight。我们来了解一下 这端代码涉及的几个变量的含义。
int mWidth:Activity窗口当前的宽度,它是由应用上一次请求WindowManagerService计算得到的,并且一直保持不变知道
下次WindowManagerService重新计算为止。
int mHeight:Activity窗口当前的高度,它是由应用上一次请求WindowManagerService计算得到的,并且一直保持不变知道
下次WindowManagerService重新计算为止。
React mWinFrame:该变量也保存了Activity窗口的宽度与高度,但是它保存的宽度与高度可能会被WindowManagerService
主动请求应用进程修改。所以你可以看到这两组值可能不相等。
该函数片段主要做了以下事情:
1 mFirst为true则表示Activity窗口是第一次请求执行策略、布局与绘制操作,Activity窗口的宽高等于当前屏幕的宽高,否
则等于mWinFrame保存的宽高。
2 当前宽高不等于上次计算的宽高,则说明窗口大小发生了变化,将windowResizesToFitContent置为true。1.2 在Activity窗口主动请求WindowManagerService计算窗口大小之前,对它的顶层视图进行一次测量操作。
public final class ViewRoot extends Handler implements ViewParent,
View.AttachInfo.Callbacks {
private void performTraversals() {
...
if (viewVisibilityChanged) {
attachInfo.mWindowVisibility = viewVisibility;
host.dispatchWindowVisibilityChanged(viewVisibility);
if (viewVisibility != View.VISIBLE || mNewSurfaceNeeded) {
if (mUseGL) {
destroyGL();
}
}
if (viewVisibility == View.GONE) {
// After making a window gone, we will count it as being
// shown for the first time the next time it gets focus.
mHasHadWindowFocus = false;
}
}
boolean insetsChanged = false;
if (mLayoutRequested) {
// Execute enqueued actions on every layout in case a view that was detached
// enqueued an action after being detached
getRunQueue().executeActions(attachInfo.mHandler);
//Activity窗口第一次请求执行测量、布局与绘制操作
if (mFirst) {
//1 host指向的是顶级视图,调用View.fitSystemWindows设置它4个内边距
//mPaddingLeft,mPaddingTop,mPaddingRight,mPaddingBottom,设置的值
//为Activity窗口初始化时内容边距的大小,这样做的目的是为了在Activity窗口四周
//留下足够的区域来设置状态栏等系统窗口
host.fitSystemWindows(mAttachInfo.mContentInsets);
// make sure touch mode code executes by setting cached value
// to opposite of the added touch mode.
mAttachInfo.mInTouchMode = !mAddedTouchMode;
ensureTouchModeLocally(mAddedTouchMode);
}
//Activity窗口不是第一次请求执行测量、布局与绘制操作
else {
//2 检查WindowManagerService是否给Activity窗口设置了新的mContentInsets与mVisibleInsets
if (!mAttachInfo.mContentInsets.equals(mPendingContentInsets)) {
mAttachInfo.mContentInsets.set(mPendingContentInsets);
//mContentInsets发生变化,则重新设置顶层视图View的内容边距
host.fitSystemWindows(mAttachInfo.mContentInsets);
insetsChanged = true;
if (DEBUG_LAYOUT) Log.v(TAG, "Content insets changing to: "
+ mAttachInfo.mContentInsets);
}
if (!mAttachInfo.mVisibleInsets.equals(mPendingVisibleInsets)) {
mAttachInfo.mVisibleInsets.set(mPendingVisibleInsets);
if (DEBUG_LAYOUT) Log.v(TAG, "Visible insets changing to: "
+ mAttachInfo.mVisibleInsets);
}
//当Activity窗口的宽高参数都被设置为WRAP_CONTENT时,标明Activity窗口的大小
//要等于内容区域的大小,由于Activity窗口的大小是要覆盖整个屏幕的,所以它的宽
//高还是被设置成屏幕的宽高。也就是说我们将Activity窗口的宽高设置为WRAP_CONTENT时
//它实际上等于屏幕的宽高。
if (lp.width == ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT
|| lp.height == ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
windowResizesToFitContent = true;
DisplayMetrics packageMetrics =
mView.getContext().getResources().getDisplayMetrics();
desiredWindowWidth = packageMetrics.widthPixels;
desiredWindowHeight = packageMetrics.heightPixels;
}
}
//根据当前窗口的宽度与宽度测量规范获取它的顶层视图的测量规范
childWidthMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(desiredWindowWidth, lp.width);
//根据Activity窗口的高度与高度测量规范获取它的顶层视图的测量规范
childHeightMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(desiredWindowHeight, lp.height);
// Ask host how big it wants to be
if (DEBUG_ORIENTATION || DEBUG_LAYOUT) Log.v(TAG,
"Measuring " + host + " in display " + desiredWindowWidth
+ "x" + desiredWindowHeight + "...");
//3 对顶层视图host进行测量
host.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
if (DBG) {
System.out.println("======================================");
System.out.println("performTraversals -- after measure");
host.debug();
}
}
if (attachInfo.mRecomputeGlobalAttributes) {
//Log.i(TAG, "Computing screen on!");
attachInfo.mRecomputeGlobalAttributes = false;
boolean oldVal = attachInfo.mKeepScreenOn;
attachInfo.mKeepScreenOn = false;
host.dispatchCollectViewAttributes(0);
if (attachInfo.mKeepScreenOn != oldVal) {
params = lp;
//Log.i(TAG, "Keep screen on changed: " + attachInfo.mKeepScreenOn);
}
}
if (mFirst || attachInfo.mViewVisibilityChanged) {
attachInfo.mViewVisibilityChanged = false;
int resizeMode = mSoftInputMode &
WindowManager.LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_MASK_ADJUST;
//根据Activity的resizeMode属性来调整窗口大小
// If we are in auto resize mode, then we need to determine
// what mode to use now.
if (resizeMode == WindowManager.LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_ADJUST_UNSPECIFIED) {
final int N = attachInfo.mScrollContainers.size();
for (int i=0; i<N; i++) {
if (attachInfo.mScrollContainers.get(i).isShown()) {
resizeMode = WindowManager.LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_ADJUST_RESIZE;
}
}
if (resizeMode == 0) {
resizeMode = WindowManager.LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_ADJUST_PAN;
}
if ((lp.softInputMode &
WindowManager.LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_MASK_ADJUST) != resizeMode) {
lp.softInputMode = (lp.softInputMode &
~WindowManager.LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_MASK_ADJUST) |
resizeMode;
params = lp;
}
}
}
if (params != null && (host.mPrivateFlags & View.REQUEST_TRANSPARENT_REGIONS) != 0) {
if (!PixelFormat.formatHasAlpha(params.format)) {
params.format = PixelFormat.TRANSLUCENT;
}
}
...
}
}我们先来了解一下本小段函数牵扯的几个变量的含义:
final Rect mPendingVisibleInsets = new Rect():可见边距大小,由WindowManagerService主动请求Activity窗口设置。
final Rect mPendingContentInsets = new Rect():内容边距大小,由WindowManagerService主动请求Activity窗口设置。
final View.AttachInfo mAttachInfo;:用来描述Activity窗口的属性,它内部也有mPendingVisibleInsets与
mPendingContentInsets属性,它用来描述Activity窗口上一次请求WindowManagerService计算得到的窗口属性值。这一段代码主要做了Activity窗口的顶层视图的测量:
1 Activity窗口第一次请求执行测量、布局与绘制操作(mFirst = true)
调用View.fitSystemWindows设置它4个内边距mPaddingLeft,mPaddingTop,mPaddingRight,mPaddingBottom,
设置的值为Activity窗口初始化时内容边距的大小,这样做的目的是为了在Activity窗口四周留下足够的区域来设置状态栏
等系统窗口。
Activity窗口不是第一次请求执行测量、布局与绘制操作(mFirst = false)
检查WindowManagerService是否给Activity窗口设置了新的mContentInsets与mVisibleInsets,如果设置了则更新
mAttachInfo里面对应的值,并更新顶层视图host的内容边距。
2 根据当前窗口的宽度与宽度测量规范获取它的顶层视图的测量规范childWidthMeasureSpec,根据Activity窗口的高度与
高度测量规范获取它的顶层视图的测量规范childHeightMeasureSpec,利用childWidthMeasureSpec与
childHeightMeasureSpec对顶层视图host进行测量。1.3 检查是否需要处理Activity窗口大小变化事件以及Activity窗口是否需要指定额外的内容边距与可见边距
public final class ViewRoot extends Handler implements ViewParent,
View.AttachInfo.Callbacks {
private void performTraversals() {
...
boolean windowShouldResize = mLayoutRequested && windowResizesToFitContent
&& ((mWidth != host.mMeasuredWidth || mHeight != host.mMeasuredHeight)
|| (lp.width == ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT &&
frame.width() < desiredWindowWidth && frame.width() != mWidth)
|| (lp.height == ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT &&
frame.height() < desiredWindowHeight && frame.height() != mHeight));
final boolean computesInternalInsets =
attachInfo.mTreeObserver.hasComputeInternalInsetsListeners();
...
}
}这段函数主要做了两件事情:
1 检查是否需要处理Activity窗口大小变化事件,以下情形以下windowShouldResize被置为true,需要处理。
1 ViewRoot.mLayoutRequested = true,说明应用正在请求Activity窗口执行一次测量、布局与绘制操作。
2 ViewRoot.windowResizesToFitContent = true,说明我们前面的代码检查到了Activity窗口的大小发生了辩护。
3 如果测量出来的大小与当前的大小不相等时也认为窗口大小发生了变化。2 检查Activity窗口是否需要指定额外的内容边距与课件可见边距,之所以这么做是为了放置一些额外的东西。
1.4 调用View.measure()完成Activity窗口的测量工作
public final class ViewRoot extends Handler implements ViewParent,
View.AttachInfo.Callbacks {
private void performTraversals() {
...
boolean insetsPending = false;
int relayoutResult = 0;
if (mFirst || windowShouldResize || insetsChanged
|| viewVisibilityChanged || params != null) {
if (viewVisibility == View.VISIBLE) {
// If this window is giving internal insets to the window
// manager, and it is being added or changing its visibility,
// then we want to first give the window manager "fake"
// insets to cause it to effectively ignore the content of
// the window during layout. This avoids it briefly causing
// other windows to resize/move based on the raw frame of the
// window, waiting until we can finish laying out this window
// and get back to the window manager with the ultimately
// computed insets.
//insetsPending = true表示Activity窗口有额外的内容边距与可见边距等待指定
insetsPending = computesInternalInsets
&& (mFirst || viewVisibilityChanged);
if (mWindowAttributes.memoryType == WindowManager.LayoutParams.MEMORY_TYPE_GPU) {
if (params == null) {
params = mWindowAttributes;
}
mGlWanted = true;
}
}
if (mSurfaceHolder != null) {
mSurfaceHolder.mSurfaceLock.lock();
mDrawingAllowed = true;
}
boolean initialized = false;
boolean contentInsetsChanged = false;
boolean visibleInsetsChanged;
boolean hadSurface = mSurface.isValid();
try {
int fl = 0;
if (params != null) {
fl = params.flags;
if (attachInfo.mKeepScreenOn) {
params.flags |= WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_KEEP_SCREEN_ON;
}
}
if (DEBUG_LAYOUT) {
Log.i(TAG, "host=w:" + host.mMeasuredWidth + ", h:" +
host.mMeasuredHeight + ", params=" + params);
}
//调用relayoutWindow()方法来请求WindowManagerService来计算Activity窗口的大小
//以及内容边距和可见边距大小,计算完毕后Activity窗口的大小会保存在变量mWinFrame中
//Activity窗口的内容边距大小保存在mPendingContentInsets中,可见边距保存中mPending
//VisibleInsets中
relayoutResult = relayoutWindow(params, viewVisibility, insetsPending);
if (params != null) {
params.flags = fl;
}
if (DEBUG_LAYOUT) Log.v(TAG, "relayout: frame=" + frame.toShortString()
+ " content=" + mPendingContentInsets.toShortString()
+ " visible=" + mPendingVisibleInsets.toShortString()
+ " surface=" + mSurface);
if (mPendingConfiguration.seq != 0) {
if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Log.v(TAG, "Visible with new config: "
+ mPendingConfiguration);
updateConfiguration(mPendingConfiguration, !mFirst);
mPendingConfiguration.seq = 0;
}
//Activity窗口内容边距是否发生变化
contentInsetsChanged = !mPendingContentInsets.equals(
mAttachInfo.mContentInsets);
//Activity窗口可见边距是否发生变化
visibleInsetsChanged = !mPendingVisibleInsets.equals(
mAttachInfo.mVisibleInsets);
if (contentInsetsChanged) {
mAttachInfo.mContentInsets.set(mPendingContentInsets);
host.fitSystemWindows(mAttachInfo.mContentInsets);
if (DEBUG_LAYOUT) Log.v(TAG, "Content insets changing to: "
+ mAttachInfo.mContentInsets);
}
if (visibleInsetsChanged) {
mAttachInfo.mVisibleInsets.set(mPendingVisibleInsets);
if (DEBUG_LAYOUT) Log.v(TAG, "Visible insets changing to: "
+ mAttachInfo.mVisibleInsets);
}
if (!hadSurface) {
if (mSurface.isValid()) {
// If we are creating a new surface, then we need to
// completely redraw it. Also, when we get to the
// point of drawing it we will hold off and schedule
// a new traversal instead. This is so we can tell the
// window manager about all of the windows being displayed
// before actually drawing them, so it can display then
// all at once.
newSurface = true;
fullRedrawNeeded = true;
mPreviousTransparentRegion.setEmpty();
if (mGlWanted && !mUseGL) {
initializeGL();
initialized = mGlCanvas != null;
}
}
} else if (!mSurface.isValid()) {
// If the surface has been removed, then reset the scroll
// positions.
mLastScrolledFocus = null;
mScrollY = mCurScrollY = 0;
if (mScroller != null) {
mScroller.abortAnimation();
}
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
if (DEBUG_ORIENTATION) Log.v(
TAG, "Relayout returned: frame=" + frame + ", surface=" + mSurface);
attachInfo.mWindowLeft = frame.left;
attachInfo.mWindowTop = frame.top;
// !!FIXME!! This next section handles the case where we did not get the
// window size we asked for. We should avoid this by getting a maximum size from
// the window session beforehand.
mWidth = frame.width();
mHeight = frame.height();
if (mSurfaceHolder != null) {
// The app owns the surface; tell it about what is going on.
if (mSurface.isValid()) {
// XXX .copyFrom() doesn't work!
//mSurfaceHolder.mSurface.copyFrom(mSurface);
mSurfaceHolder.mSurface = mSurface;
}
mSurfaceHolder.mSurfaceLock.unlock();
if (mSurface.isValid()) {
if (!hadSurface) {
mSurfaceHolder.ungetCallbacks();
mIsCreating = true;
mSurfaceHolderCallback.surfaceCreated(mSurfaceHolder);
SurfaceHolder.Callback callbacks[] = mSurfaceHolder.getCallbacks();
if (callbacks != null) {
for (SurfaceHolder.Callback c : callbacks) {
c.surfaceCreated(mSurfaceHolder);
}
}
surfaceChanged = true;
}
if (surfaceChanged) {
mSurfaceHolderCallback.surfaceChanged(mSurfaceHolder,
lp.format, mWidth, mHeight);
SurfaceHolder.Callback callbacks[] = mSurfaceHolder.getCallbacks();
if (callbacks != null) {
for (SurfaceHolder.Callback c : callbacks) {
c.surfaceChanged(mSurfaceHolder, lp.format,
mWidth, mHeight);
}
}
}
mIsCreating = false;
} else if (hadSurface) {
mSurfaceHolder.ungetCallbacks();
SurfaceHolder.Callback callbacks[] = mSurfaceHolder.getCallbacks();
mSurfaceHolderCallback.surfaceDestroyed(mSurfaceHolder);
if (callbacks != null) {
for (SurfaceHolder.Callback c : callbacks) {
c.surfaceDestroyed(mSurfaceHolder);
}
}
mSurfaceHolder.mSurfaceLock.lock();
// Make surface invalid.
//mSurfaceHolder.mSurface.copyFrom(mSurface);
mSurfaceHolder.mSurface = new Surface();
mSurfaceHolder.mSurfaceLock.unlock();
}
}
if (initialized) {
mGlCanvas.setViewport((int) (mWidth * appScale + 0.5f),
(int) (mHeight * appScale + 0.5f));
}
//检查是否需要重新测量Activity窗口的大小
boolean focusChangedDueToTouchMode = ensureTouchModeLocally(
(relayoutResult&WindowManagerImpl.RELAYOUT_IN_TOUCH_MODE) != 0);
if (focusChangedDueToTouchMode || mWidth != host.mMeasuredWidth
|| mHeight != host.mMeasuredHeight || contentInsetsChanged) {
childWidthMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(mWidth, lp.width);
childHeightMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(mHeight, lp.height);
if (DEBUG_LAYOUT) Log.v(TAG, "Ooops, something changed! mWidth="
+ mWidth + " measuredWidth=" + host.mMeasuredWidth
+ " mHeight=" + mHeight
+ " measuredHeight" + host.mMeasuredHeight
+ " coveredInsetsChanged=" + contentInsetsChanged);
//调用View.measure()方法进行测量
// Ask host how big it wants to be
host.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
// Implementation of weights from WindowManager.LayoutParams
// We just grow the dimensions as needed and re-measure if
// needs be
int width = host.mMeasuredWidth;
int height = host.mMeasuredHeight;
boolean measureAgain = false;
if (lp.horizontalWeight > 0.0f) {
width += (int) ((mWidth - width) * lp.horizontalWeight);
childWidthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(width,
MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
measureAgain = true;
}
if (lp.verticalWeight > 0.0f) {
height += (int) ((mHeight - height) * lp.verticalWeight);
childHeightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(height,
MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
measureAgain = true;
}
if (measureAgain) {
if (DEBUG_LAYOUT) Log.v(TAG,
"And hey let's measure once more: width=" + width
+ " height=" + height);
host.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
mLayoutRequested = true;
}
}
...
}
}先来说说这段代码前面的几个boolean值,也就是代码的执行条件:
1 mFirst = true:Activity窗口第一次执行策略、布局与绘制操作。
2 windowShouldResize = true:Activity窗口的大小发生了变化。
3 insetsChanged:Activity窗口的内容边距发生了变化。
4 viewVisibilityChanged:Activity窗口的可见性发生了变化。
5 params != null:变量params指向了一个WindowManagerParams对象,即Activity窗口的属性发生了变化。这段代码主要做了以下几件事情:
1 调用relayoutWindow()方法来请求WindowManagerService来计算Activity窗口的大小以及内容边距和可见边距大小,计算 完毕后Activity窗口的大小会保存在变量mWinFrame中Activity窗口的内容边距大小保存在mPendingContentInsets中,可见 边距保存中mPendingVisibleInsets中
2 检查是否需要重新测量Activity窗口的大小,满足以下条件之一则需要重新测量:
1 focusChangedDueToTouchMode = true:即Activity窗口的触摸模式发生了变化,由此引发了Activity窗口获得当前
焦点的控件发生了变化。
2 Activity窗口新测量出来的宽度host.mMeasuredWidth和高度host.mMeasuredHeight不等于WindowManagerService
服务计算出来的宽度mWidth和高度mHeight。
3 contentInsetsChanged = true:Activity窗口的内容边距和可见边距发生了变化。如果需要进行测量,则调用View.measure()方法进行测量。
1.5 调用View.layout()方法完成布局工作,并将Activity窗口指定的额外的内容边距与可见边距通过sWindowSession发送给WindowManagerService。
public final class ViewRoot extends Handler implements ViewParent,
View.AttachInfo.Callbacks {
private void performTraversals() {
...
final boolean didLayout = mLayoutRequested;
boolean triggerGlobalLayoutListener = didLayout
|| attachInfo.mRecomputeGlobalAttributes;
if (didLayout) {
mLayoutRequested = false;
mScrollMayChange = true;
if (DEBUG_ORIENTATION || DEBUG_LAYOUT) Log.v(
TAG, "Laying out " + host + " to (" +
host.mMeasuredWidth + ", " + host.mMeasuredHeight + ")");
long startTime = 0L;
if (Config.DEBUG && ViewDebug.profileLayout) {
startTime = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
}
//调用View.layout()方法完成布局工作
host.layout(0, 0, host.mMeasuredWidth, host.mMeasuredHeight);
if (Config.DEBUG && ViewDebug.consistencyCheckEnabled) {
if (!host.dispatchConsistencyCheck(ViewDebug.CONSISTENCY_LAYOUT)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("The view hierarchy is an inconsistent state,"
+ "please refer to the logs with the tag "
+ ViewDebug.CONSISTENCY_LOG_TAG + " for more infomation.");
}
}
if (Config.DEBUG && ViewDebug.profileLayout) {
EventLog.writeEvent(60001, SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - startTime);
}
// By this point all views have been sized and positionned
// We can compute the transparent area
if ((host.mPrivateFlags & View.REQUEST_TRANSPARENT_REGIONS) != 0) {
// start out transparent
// TODO: AVOID THAT CALL BY CACHING THE RESULT?
host.getLocationInWindow(mTmpLocation);
mTransparentRegion.set(mTmpLocation[0], mTmpLocation[1],
mTmpLocation[0] + host.mRight - host.mLeft,
mTmpLocation[1] + host.mBottom - host.mTop);
host.gatherTransparentRegion(mTransparentRegion);
if (mTranslator != null) {
mTranslator.translateRegionInWindowToScreen(mTransparentRegion);
}
if (!mTransparentRegion.equals(mPreviousTransparentRegion)) {
mPreviousTransparentRegion.set(mTransparentRegion);
// reconfigure window manager
try {
sWindowSession.setTransparentRegion(mWindow, mTransparentRegion);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
}
}
if (DBG) {
System.out.println("======================================");
System.out.println("performTraversals -- after setFrame");
host.debug();
}
}
if (triggerGlobalLayoutListener) {
attachInfo.mRecomputeGlobalAttributes = false;
attachInfo.mTreeObserver.dispatchOnGlobalLayout();
}
//computesInternalInsets为true时表明Activity窗口指定了额外的内容边距与可见边距,这个时候需要
//通知WindowManagerService,以便WindowManagerService下次可以知道Activity的真实布局。
if (computesInternalInsets) {
ViewTreeObserver.InternalInsetsInfo insets = attachInfo.mGivenInternalInsets;
final Rect givenContent = attachInfo.mGivenInternalInsets.contentInsets;
final Rect givenVisible = attachInfo.mGivenInternalInsets.visibleInsets;
givenContent.left = givenContent.top = givenContent.right
= givenContent.bottom = givenVisible.left = givenVisible.top
= givenVisible.right = givenVisible.bottom = 0;
//调用TreeObserver.dispatchOnComputeInternalInsets(insets)来计算Activity窗口额外指定的
//内容边距与可见边距的大小,计算完成后保存在变量attachInfo.mGivenInternalInsets中。
attachInfo.mTreeObserver.dispatchOnComputeInternalInsets(insets);
Rect contentInsets = insets.contentInsets;
Rect visibleInsets = insets.visibleInsets;
if (mTranslator != null) {
contentInsets = mTranslator.getTranslatedContentInsets(contentInsets);
visibleInsets = mTranslator.getTranslatedVisbileInsets(visibleInsets);
}
if (insetsPending || !mLastGivenInsets.equals(insets)) {
mLastGivenInsets.set(insets);
try {
//sWindowSession是一个Binder代理对象,通过它将内容边距与可见边距设置到WindowManagerService中
sWindowSession.setInsets(mWindow, insets.mTouchableInsets,
contentInsets, visibleInsets);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
}
}
if (mFirst) {
// handle first focus request
if (DEBUG_INPUT_RESIZE) Log.v(TAG, "First: mView.hasFocus()="
+ mView.hasFocus());
if (mView != null) {
if (!mView.hasFocus()) {
mView.requestFocus(View.FOCUS_FORWARD);
mFocusedView = mRealFocusedView = mView.findFocus();
if (DEBUG_INPUT_RESIZE) Log.v(TAG, "First: requested focused view="
+ mFocusedView);
} else {
mRealFocusedView = mView.findFocus();
if (DEBUG_INPUT_RESIZE) Log.v(TAG, "First: existing focused view="
+ mRealFocusedView);
}
}
}
mFirst = false;
mWillDrawSoon = false;
mNewSurfaceNeeded = false;
mViewVisibility = viewVisibility;
if (mAttachInfo.mHasWindowFocus) {
final boolean imTarget = WindowManager.LayoutParams
.mayUseInputMethod(mWindowAttributes.flags);
if (imTarget != mLastWasImTarget) {
mLastWasImTarget = imTarget;
InputMethodManager imm = InputMethodManager.peekInstance();
if (imm != null && imTarget) {
imm.startGettingWindowFocus(mView);
imm.onWindowFocus(mView, mView.findFocus(),
mWindowAttributes.softInputMode,
!mHasHadWindowFocus, mWindowAttributes.flags);
}
}
}
boolean cancelDraw = attachInfo.mTreeObserver.dispatchOnPreDraw();
if (!cancelDraw && !newSurface) {
mFullRedrawNeeded = false;
draw(fullRedrawNeeded);
if ((relayoutResult&WindowManagerImpl.RELAYOUT_FIRST_TIME) != 0
|| mReportNextDraw) {
if (LOCAL_LOGV) {
Log.v(TAG, "FINISHED DRAWING: " + mWindowAttributes.getTitle());
}
mReportNextDraw = false;
if (mSurfaceHolder != null && mSurface.isValid()) {
mSurfaceHolderCallback.surfaceRedrawNeeded(mSurfaceHolder);
SurfaceHolder.Callback callbacks[] = mSurfaceHolder.getCallbacks();
if (callbacks != null) {
for (SurfaceHolder.Callback c : callbacks) {
if (c instanceof SurfaceHolder.Callback2) {
((SurfaceHolder.Callback2)c).surfaceRedrawNeeded(
mSurfaceHolder);
}
}
}
}
try {
sWindowSession.finishDrawing(mWindow);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
}
} else {
// We were supposed to report when we are done drawing. Since we canceled the
// draw, remember it here.
if ((relayoutResult&WindowManagerImpl.RELAYOUT_FIRST_TIME) != 0) {
mReportNextDraw = true;
}
if (fullRedrawNeeded) {
mFullRedrawNeeded = true;
}
// Try again
scheduleTraversals();
}
}
}这段代码调用View.layout()方法完成布局工作,并将Activity窗口指定的额外的内容边距与可见边距通过sWindowSession发送给WindowManagerService。
关键点2:WindowManagerService.relayoutWindow(Session session, IWindow client, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs, int requestedWidth, int requestedHeight, int viewVisibility, boolean insetsPending, Rect outFrame, Rect outContentInsets, Rect outVisibleInsets, Configuration outConfig, Surface outSurface)
public class WindowManagerService extends IWindowManager.Stub
implements Watchdog.Monitor {
public int relayoutWindow(Session session, IWindow client,
WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs, int requestedWidth,
int requestedHeight, int viewVisibility, boolean insetsPending,
Rect outFrame, Rect outContentInsets, Rect outVisibleInsets,
Configuration outConfig, Surface outSurface) {
boolean displayed = false;
boolean inTouchMode;
boolean configChanged;
long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
synchronized(mWindowMap) {
//client对应的是应用进程的Activity窗口,每个IWindow对象都在WindowManagerService
//端对应着一个WindowState对象,该对象描述了窗口的信息。
WindowState win = windowForClientLocked(session, client, false);
if (win == null) {
return 0;
}
//requestedWidth与requestedHeight描述的是应用进程请求设置Activity窗口的宽高
win.mRequestedWidth = requestedWidth;
win.mRequestedHeight = requestedHeight;
if (attrs != null) {
mPolicy.adjustWindowParamsLw(attrs);
}
int attrChanges = 0;
int flagChanges = 0;
if (attrs != null) {
//win.mAttrs指向的是WindowManager.LayoutParams,它描述了Activity窗口的布局参数
flagChanges = win.mAttrs.flags ^= attrs.flags;
attrChanges = win.mAttrs.copyFrom(attrs);
}
if (DEBUG_LAYOUT) Slog.v(TAG, "Relayout " + win + ": " + win.mAttrs);
//透明度
if ((attrChanges & WindowManager.LayoutParams.ALPHA_CHANGED) != 0) {
win.mAlpha = attrs.alpha;
}
final boolean scaledWindow =
((win.mAttrs.flags & WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_SCALED) != 0);
//宽高缩放因子
if (scaledWindow) {
// requested{Width|Height} Surface's physical size
// attrs.{width|height} Size on screen
win.mHScale = (attrs.width != requestedWidth) ?
(attrs.width / (float)requestedWidth) : 1.0f;
win.mVScale = (attrs.height != requestedHeight) ?
(attrs.height / (float)requestedHeight) : 1.0f;
} else {
win.mHScale = win.mVScale = 1;
}
//窗口焦点变化
boolean imMayMove = (flagChanges&(
WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_ALT_FOCUSABLE_IM |
WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_FOCUSABLE)) != 0;
boolean focusMayChange = win.mViewVisibility != viewVisibility
|| ((flagChanges&WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_FOCUSABLE) != 0)
|| (!win.mRelayoutCalled);
boolean wallpaperMayMove = win.mViewVisibility != viewVisibility
&& (win.mAttrs.flags & FLAG_SHOW_WALLPAPER) != 0;
win.mRelayoutCalled = true;
//窗口可见性
final int oldVisibility = win.mViewVisibility;
win.mViewVisibility = viewVisibility;
if (viewVisibility == View.VISIBLE &&
(win.mAppToken == null || !win.mAppToken.clientHidden)) {
displayed = !win.isVisibleLw();
if (win.mExiting) {
win.mExiting = false;
win.mAnimation = null;
}
if (win.mDestroying) {
win.mDestroying = false;
mDestroySurface.remove(win);
}
if (oldVisibility == View.GONE) {
win.mEnterAnimationPending = true;
}
if (displayed) {
if (win.mSurface != null && !win.mDrawPending
&& !win.mCommitDrawPending && !mDisplayFrozen
&& mPolicy.isScreenOn()) {
//窗口进入动画
applyEnterAnimationLocked(win);
}
if ((win.mAttrs.flags
& WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_TURN_SCREEN_ON) != 0) {
if (DEBUG_VISIBILITY) Slog.v(TAG,
"Relayout window turning screen on: " + win);
win.mTurnOnScreen = true;
}
int diff = 0;
if (win.mConfiguration != mCurConfiguration
&& (win.mConfiguration == null
|| (diff=mCurConfiguration.diff(win.mConfiguration)) != 0)) {
win.mConfiguration = mCurConfiguration;
if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) {
Slog.i(TAG, "Window " + win + " visible with new config: "
+ win.mConfiguration + " / 0x"
+ Integer.toHexString(diff));
}
outConfig.setTo(mCurConfiguration);
}
}
if ((attrChanges&WindowManager.LayoutParams.FORMAT_CHANGED) != 0) {
// To change the format, we need to re-build the surface.
win.destroySurfaceLocked();
displayed = true;
}
try {
//创建Surface画布
Surface surface = win.createSurfaceLocked();
if (surface != null) {
outSurface.copyFrom(surface);
win.mReportDestroySurface = false;
win.mSurfacePendingDestroy = false;
if (SHOW_TRANSACTIONS) Slog.i(TAG,
" OUT SURFACE " + outSurface + ": copied");
} else {
// For some reason there isn't a surface. Clear the
// caller's object so they see the same state.
outSurface.release();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
mInputMonitor.updateInputWindowsLw();
Slog.w(TAG, "Exception thrown when creating surface for client "
+ client + " (" + win.mAttrs.getTitle() + ")",
e);
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
return 0;
}
if (displayed) {
focusMayChange = true;
}
if (win.mAttrs.type == TYPE_INPUT_METHOD
&& mInputMethodWindow == null) {
mInputMethodWindow = win;
imMayMove = true;
}
if (win.mAttrs.type == TYPE_BASE_APPLICATION
&& win.mAppToken != null
&& win.mAppToken.startingWindow != null) {
// Special handling of starting window over the base
// window of the app: propagate lock screen flags to it,
// to provide the correct semantics while starting.
final int mask =
WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_SHOW_WHEN_LOCKED
| WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_DISMISS_KEYGUARD
| WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_ALLOW_LOCK_WHILE_SCREEN_ON;
WindowManager.LayoutParams sa = win.mAppToken.startingWindow.mAttrs;
sa.flags = (sa.flags&~mask) | (win.mAttrs.flags&mask);
}
} else {
win.mEnterAnimationPending = false;
if (win.mSurface != null) {
if (DEBUG_VISIBILITY) Slog.i(TAG, "Relayout invis " + win
+ ": mExiting=" + win.mExiting
+ " mSurfacePendingDestroy=" + win.mSurfacePendingDestroy);
// If we are not currently running the exit animation, we
// need to see about starting one.
if (!win.mExiting || win.mSurfacePendingDestroy) {
// Try starting an animation; if there isn't one, we
// can destroy the surface right away.
int transit = WindowManagerPolicy.TRANSIT_EXIT;
if (win.getAttrs().type == TYPE_APPLICATION_STARTING) {
transit = WindowManagerPolicy.TRANSIT_PREVIEW_DONE;
}
if (!win.mSurfacePendingDestroy && win.isWinVisibleLw() &&
applyAnimationLocked(win, transit, false)) {
focusMayChange = true;
win.mExiting = true;
} else if (win.isAnimating()) {
// Currently in a hide animation... turn this into
// an exit.
win.mExiting = true;
} else if (win == mWallpaperTarget) {
// If the wallpaper is currently behind this
// window, we need to change both of them inside
// of a transaction to avoid artifacts.
win.mExiting = true;
win.mAnimating = true;
} else {
if (mInputMethodWindow == win) {
mInputMethodWindow = null;
}
win.destroySurfaceLocked();
}
}
}
if (win.mSurface == null || (win.getAttrs().flags
& WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_KEEP_SURFACE_WHILE_ANIMATING) == 0
|| win.mSurfacePendingDestroy) {
// We are being called from a local process, which
// means outSurface holds its current surface. Ensure the
// surface object is cleared, but we don't want it actually
// destroyed at this point.
win.mSurfacePendingDestroy = false;
outSurface.release();
if (DEBUG_VISIBILITY) Slog.i(TAG, "Releasing surface in: " + win);
} else if (win.mSurface != null) {
if (DEBUG_VISIBILITY) Slog.i(TAG,
"Keeping surface, will report destroy: " + win);
win.mReportDestroySurface = true;
outSurface.copyFrom(win.mSurface);
}
}
if (focusMayChange) {
//System.out.println("Focus may change: " + win.mAttrs.getTitle());
if (updateFocusedWindowLocked(UPDATE_FOCUS_WILL_PLACE_SURFACES)) {
imMayMove = false;
}
//System.out.println("Relayout " + win + ": focus=" + mCurrentFocus);
}
// updateFocusedWindowLocked() already assigned layers so we only need to
// reassign them at this point if the IM window state gets shuffled
boolean assignLayers = false;
if (imMayMove) {
if (moveInputMethodWindowsIfNeededLocked(false) || displayed) {
// Little hack here -- we -should- be able to rely on the
// function to return true if the IME has moved and needs
// its layer recomputed. However, if the IME was hidden
// and isn't actually moved in the list, its layer may be
// out of data so we make sure to recompute it.
assignLayers = true;
}
}
if (wallpaperMayMove) {
if ((adjustWallpaperWindowsLocked()&ADJUST_WALLPAPER_LAYERS_CHANGED) != 0) {
assignLayers = true;
}
}
mLayoutNeeded = true;
win.mGivenInsetsPending = insetsPending;
if (assignLayers) {
assignLayersLocked();
}
configChanged = updateOrientationFromAppTokensLocked();
//计算参数client描述的窗口的大小
performLayoutAndPlaceSurfacesLocked();
if (displayed && win.mIsWallpaper) {
updateWallpaperOffsetLocked(win, mDisplay.getWidth(),
mDisplay.getHeight(), false);
}
if (win.mAppToken != null) {
win.mAppToken.updateReportedVisibilityLocked();
}
outFrame.set(win.mFrame);
outContentInsets.set(win.mContentInsets);
outVisibleInsets.set(win.mVisibleInsets);
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(
TAG, "Relayout given client " + client.asBinder()
+ ", requestedWidth=" + requestedWidth
+ ", requestedHeight=" + requestedHeight
+ ", viewVisibility=" + viewVisibility
+ "\nRelayout returning frame=" + outFrame
+ ", surface=" + outSurface);
if (localLOGV || DEBUG_FOCUS) Slog.v(
TAG, "Relayout of " + win + ": focusMayChange=" + focusMayChange);
inTouchMode = mInTouchMode;
mInputMonitor.updateInputWindowsLw();
}
if (configChanged) {
sendNewConfiguration();
}
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
return (inTouchMode ? WindowManagerImpl.RELAYOUT_IN_TOUCH_MODE : 0)
| (displayed ? WindowManagerImpl.RELAYOUT_FIRST_TIME : 0);
}
}这个函数参数有点多,我们来分析下各个参数的含义:
IWindow window:Activity窗口的唯一标识,用于与其他窗口区别开来。
WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs:布局规范LayoutParams
int requestedWidth, int requestedHeight:Activity窗口经过测量后得到的宽度与高度,另外,传递给
ActivityManagerService的宽高以及考虑了Activity窗口所设置的缩放因子了。
int viewFlags:Activity窗口的可见状态
boolean insetsPending:Activity窗口是否指定额外的内容边距与可见边距。
Rect outFrame:输出参数,用来保存WindowManagerService计算得出的窗口大小。
Rect outContentInsets:输出参数,用来保存WindowManagerService计算得出的内容边距的大小。
Rect outVisibleInsets:输出参数,用来保存WindowManagerService计算得出的可见边距的大小。
Configuration outConfig:输出参数,用来保存WindowManagerService返回来的配置信息。
Surface outSurface:输出参数,用来保存WindowManagerService返回给Activity的绘图画布。这个方法的实现也比较长,它主要做了以下几件事情:
- 如果系统当前获得焦点的窗口可能发生了变化,那么就会调用成员函数updateFocusedWindowLocked来重新计算系统当前应该获得焦点的窗口。如果系统当前获得焦点的窗口真的发生了变化,即窗口堆栈的窗口 排列发生了变化,那么在调用成员函数updateFocusedWindowLocked的时候,就会调用成员函数assignLayersLocked来重新计算系统中所有窗口的Z轴位置。
- 如果系统中的输入法窗口可能需要移动,那么就会调用成员函数moveInputMethodWindowsIfNeededLocked来检查是否真的需要移动输入法窗口。如果需要移动,那么成员函 数moveInputMethodWindowsIfNeededLocked的返回值就会等于true,这时候就说明输入法窗口在窗口堆栈中的位置发生了变化,因此,就会将变量assignLayers的值设置为true,表示接下来需要重新计算 系统中所有窗口的Z轴位置。
- 如果当前正在请求调整其布局的窗口是由不可见变化可见的,即变量displayed的值等于true,那么接下来也是需要重新计算系统中所有窗口的Z轴位置的,因此,就会将assignLayers的值设置为true。
- 如果系统中的壁纸窗口可能需要移动,那么就会调用成员函数adjustWallpaperWindowsLocked来检查是否真的需要移动壁纸窗口。如果需要移动,那么成员函数adjustWallpaperWindowsLocked的返回值 的ADJUST_WALLPAPER_LAYERS_CHANGED位就会等于1,这时候就说明壁纸窗口在窗口堆栈中的位置发生了变化,因此,就会将变量assignLayers的值设置为true,表示接下来需要重新计算系统中所有窗口的Z轴位置。
经过上述的一系列操作后,如果得到的变量assignLayers的值设置等于true,那么WindowManagerService类的成员函数relayoutWindow就会调用成员函数assignLayersLocked来重新计算系统中所有窗口的Z轴位置。
该函数继续调用performLayoutAndPlaceSurfacesLocked()方法来计算client所描述的窗口的大小,计算完成后窗口的宽高、内容边距 与可见边距分别保存在WindowState对象的mFrame、mContentInsets与mVisibleInsets中。我们接着来看performLayoutAndPlaceSurfacesLocked() 方法的实现。
关键点3:WindowManagerService.performLayoutAndPlaceSurfacesLocked()
public class WindowManagerService extends IWindowManager.Stub
implements Watchdog.Monitor {
private boolean mInLayout = false;
private final void performLayoutAndPlaceSurfacesLocked() {
if (mInLayout) {
if (DEBUG) {
throw new RuntimeException("Recursive call!");
}
Slog.w(TAG, "performLayoutAndPlaceSurfacesLocked called while in layout");
return;
}
if (mWaitingForConfig) {
// Our configuration has changed (most likely rotation), but we
// don't yet have the complete configuration to report to
// applications. Don't do any window layout until we have it.
return;
}
if (mDisplay == null) {
// Not yet initialized, nothing to do.
return;
}
boolean recoveringMemory = false;
if (mForceRemoves != null) {
recoveringMemory = true;
//检查是否存在需要强制删除的窗口,在系统内存不足的情况下,一些窗口会被回收,
//这些窗口会保存在列表mForceRemoves中。
// Wait a little it for things to settle down, and off we go.
for (int i=0; i<mForceRemoves.size(); i++) {
WindowState ws = mForceRemoves.get(i);
Slog.i(TAG, "Force removing: " + ws);
//调用removeWindowInnerLocked()方法移除窗口
removeWindowInnerLocked(ws.mSession, ws);
}
mForceRemoves = null;
Slog.w(TAG, "Due to memory failure, waiting a bit for next layout");
Object tmp = new Object();
synchronized (tmp) {
try {
tmp.wait(250);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
}
mInLayout = true;
try {
performLayoutAndPlaceSurfacesLockedInner(recoveringMemory);
//检查是否有窗口需要被移除,如果需要则调用removeWindowInnerLocked()方法移除窗口
//移除窗口后并没有回收内存,只有在内存不足时才会回收这些内存。
int i = mPendingRemove.size()-1;
if (i >= 0) {
while (i >= 0) {
WindowState w = mPendingRemove.get(i);
removeWindowInnerLocked(w.mSession, w);
i--;
}
mPendingRemove.clear();
//设置标志位防止performLayoutAndPlaceSurfacesLockedInner方法重复被调用
mInLayout = false;
assignLayersLocked();
mLayoutNeeded = true;
performLayoutAndPlaceSurfacesLocked();
} else {
mInLayout = false;
if (mLayoutNeeded) {
requestAnimationLocked(0);
}
}
if (mWindowsChanged && !mWindowChangeListeners.isEmpty()) {
mH.removeMessages(H.REPORT_WINDOWS_CHANGE);
mH.sendMessage(mH.obtainMessage(H.REPORT_WINDOWS_CHANGE));
}
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
mInLayout = false;
Slog.e(TAG, "Unhandled exception while layout out windows", e);
}
}
}该方法会进一步调用方法performLayoutAndPlaceSurfacesLockedInner(recoveringMemory)来完成它的工作。
在调用之前:
检查是否存在需要强制删除的窗口,在系统内存不足的情况下,一些窗口会被回收,这些窗口会保存在列表mForceRemoves中。调用方法removeWindowInnerLocked 移除这些窗口。
在调用之后:
检查系统中是否有窗口需要移除,如果有则调用方法removeWindowInnerLocked移除这些窗口,移除窗口后并没有回收内存,只有在内存不足时才会回收这些内存。
另外,移除窗口的流程也是比较复杂的,先要将窗口从WindowManagerService的相关成员变量中移除,然后将壁纸窗口与输入法窗口调整到合适的Z 轴位置上,以便可以被下个窗口利用,最后调整剩下窗口在Z轴上的位置,以便可以正确的反应系统UI的状态。
接下来我们来分析performLayoutAndPlaceSurfacesLockedInner()函数的实现,这个函数不仅名字长,实现也非常长,足足有1200多行。
关键点4:WindowManagerService.performLayoutAndPlaceSurfacesLockedInner( boolean recoveringMemory)
从这个performLayoutAndPlaceSurfacesLocked长长的方法名字可以看出,它不仅仅用来计算窗口大小,它还负责刷新系统UI,事实上,每当 Activity窗口属性发生了变化,例如:可见性,大小等,又或者它要新增、删除子视图时,都会要求WindowManagerService刷新系统UI,所以 你可以看出WindowManagerService的主要工作就是刷新系统UI,
public class WindowManagerService extends IWindowManager.Stub
implements Watchdog.Monitor {
private final void performLayoutAndPlaceSurfacesLockedInner(
boolean recoveringMemory) {
...
final long currentTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
//获取当前屏幕的宽高
final int dw = mDisplay.getWidth();
final int dh = mDisplay.getHeight();
int i;
//更新窗口焦点
if (mFocusMayChange) {
mFocusMayChange = false;
updateFocusedWindowLocked(UPDATE_FOCUS_WILL_PLACE_SURFACES);
}
// Initialize state of exiting tokens.
for (i=mExitingTokens.size()-1; i>=0; i--) {
mExitingTokens.get(i).hasVisible = false;
}
// Initialize state of exiting applications.
for (i=mExitingAppTokens.size()-1; i>=0; i--) {
mExitingAppTokens.get(i).hasVisible = false;
}
boolean orientationChangeComplete = true;
Session holdScreen = null;
float screenBrightness = -1;
float buttonBrightness = -1;
boolean focusDisplayed = false;
boolean animating = false;
boolean createWatermark = false;
if (mFxSession == null) {
mFxSession = new SurfaceSession();
createWatermark = true;
}
if (SHOW_TRANSACTIONS) Slog.i(TAG, ">>> OPEN TRANSACTION");
//这个一个native方法,用来开启SurfaceFlinger事物
Surface.openTransaction();
if (createWatermark) {
createWatermark();
}
if (mWatermark != null) {
mWatermark.positionSurface(dw, dh);
}
try {
boolean wallpaperForceHidingChanged = false;
int repeats = 0;
int changes = 0;
//创建一个最多执行7次的while循环,计算窗口的大小以及执行窗口动画
do {
repeats++;
if (repeats > 6) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Animation repeat aborted after too many iterations");
mLayoutNeeded = false;
break;
}
if ((changes&(WindowManagerPolicy.FINISH_LAYOUT_REDO_WALLPAPER
| WindowManagerPolicy.FINISH_LAYOUT_REDO_CONFIG
| WindowManagerPolicy.FINISH_LAYOUT_REDO_LAYOUT)) != 0) {
if ((changes&WindowManagerPolicy.FINISH_LAYOUT_REDO_WALLPAPER) != 0) {
if ((adjustWallpaperWindowsLocked()&ADJUST_WALLPAPER_LAYERS_CHANGED) != 0) {
assignLayersLocked();
mLayoutNeeded = true;
}
}
if ((changes&WindowManagerPolicy.FINISH_LAYOUT_REDO_CONFIG) != 0) {
if (DEBUG_LAYOUT) Slog.v(TAG, "Computing new config from layout");
if (updateOrientationFromAppTokensLocked()) {
mLayoutNeeded = true;
mH.sendEmptyMessage(H.SEND_NEW_CONFIGURATION);
}
}
if ((changes&WindowManagerPolicy.FINISH_LAYOUT_REDO_LAYOUT) != 0) {
mLayoutNeeded = true;
}
}
// FIRST LOOP: Perform a layout, if needed.
if (repeats < 4) {
changes = performLayoutLockedInner();
if (changes != 0) {
continue;
}
} else {
Slog.w(TAG, "Layout repeat skipped after too many iterations");
changes = 0;
}
...
}
}这个方法不仅名字长,实现也非常长,足足有1200多行,但它也正是WindowManagerService的核心逻辑所在。这个方法主要做了以下事情:
1 创建一个最多执行7次的while循环,在该循环中:
① 调用performLayoutLockedInner()计算各个窗口的大小。
② 处理窗口显示动画与切换动画以及更新各个窗口的可见性。
2 将窗口的属性发送给SurfaceFlinger,SurfaceFlinger会去更新Layer属性,对Layer进行可见性计算与合成等操作,最后
渲染到硬件缓冲区中去。每个窗口的属性更新操作都被封装到一个SurfaceFlinger服务的一个事务中(Transaction)。
发送给SurfaceFlinger的属性有:
① 设置窗口的大小
② 设置窗口在X轴和Y轴上的位置
③ 设置窗口在Z轴上的位置
④ 设置窗口的Alpha通道值
⑤ 设置窗口的变换矩阵
3 经过上面的操作,系统UI刷新完成,系统将执行不再显示窗口的清理工作,销毁掉不再显示窗口的绘图画布,移除窗口令牌
WindowToken与Activity窗口令牌AppWindowToken。我们这里先分析窗口大小的计算流程,即performLayoutLockedInner()函数的实现,关于窗口动画后续会有文章分析。
关键点5:WindowManagerService.performLayoutLockedInner()
public class WindowManagerService extends IWindowManager.Stub
implements Watchdog.Monitor {
final WindowManagerPolicy mPolicy = PolicyManager.makeNewWindowManager();
/**
* Z-ordered (bottom-most first) list of all Window objects.
*/
final ArrayList<WindowState> mWindows = new ArrayList<WindowState>();
private final int performLayoutLockedInner() {
if (!mLayoutNeeded) {
return 0;
}
mLayoutNeeded = false;
final int dw = mDisplay.getWidth();
final int dh = mDisplay.getHeight();
final int N = mWindows.size();
int i;
if (DEBUG_LAYOUT) Slog.v(TAG, "performLayout: needed="
+ mLayoutNeeded + " dw=" + dw + " dh=" + dh);
//调用PhoneWindowManager.beginLayoutLw()方法设置屏幕大小
mPolicy.beginLayoutLw(dw, dh);
int seq = mLayoutSeq+1;
if (seq < 0) seq = 0;
mLayoutSeq = seq;
// First perform layout of any root windows (not attached
// to another window).
int topAttached = -1;
for (i = N-1; i >= 0; i--) {
WindowState win = mWindows.get(i);
// Don't do layout of a window if it is not visible, or
// soon won't be visible, to avoid wasting time and funky
// changes while a window is animating away.
final AppWindowToken atoken = win.mAppToken;
final boolean gone = win.mViewVisibility == View.GONE
|| !win.mRelayoutCalled
|| win.mRootToken.hidden
|| (atoken != null && atoken.hiddenRequested)
|| win.mAttachedHidden
|| win.mExiting || win.mDestroying;
if (!win.mLayoutAttached) {
if (DEBUG_LAYOUT) Slog.v(TAG, "First pass " + win
+ ": gone=" + gone + " mHaveFrame=" + win.mHaveFrame
+ " mLayoutAttached=" + win.mLayoutAttached);
if (DEBUG_LAYOUT && gone) Slog.v(TAG, " (mViewVisibility="
+ win.mViewVisibility + " mRelayoutCalled="
+ win.mRelayoutCalled + " hidden="
+ win.mRootToken.hidden + " hiddenRequested="
+ (atoken != null && atoken.hiddenRequested)
+ " mAttachedHidden=" + win.mAttachedHidden);
}
// If this view is GONE, then skip it -- keep the current
// frame, and let the caller know so they can ignore it
// if they want. (We do the normal layout for INVISIBLE
// windows, since that means "perform layout as normal,
// just don't display").
if (!gone || !win.mHaveFrame) {
if (!win.mLayoutAttached) {
//调用PhoneWindowManager.layoutWindowLw()方法计算各个窗口大小
//内容边距大小以及可见边距大小
mPolicy.layoutWindowLw(win, win.mAttrs, null);
win.mLayoutSeq = seq;
if (DEBUG_LAYOUT) Slog.v(TAG, "-> mFrame="
+ win.mFrame + " mContainingFrame="
+ win.mContainingFrame + " mDisplayFrame="
+ win.mDisplayFrame);
} else {
if (topAttached < 0) topAttached = i;
}
}
}
// Now perform layout of attached windows, which usually
// depend on the position of the window they are attached to.
// XXX does not deal with windows that are attached to windows
// that are themselves attached.
for (i = topAttached; i >= 0; i--) {
WindowState win = mWindows.get(i);
// If this view is GONE, then skip it -- keep the current
// frame, and let the caller know so they can ignore it
// if they want. (We do the normal layout for INVISIBLE
// windows, since that means "perform layout as normal,
// just don't display").
if (win.mLayoutAttached) {
if (DEBUG_LAYOUT) Slog.v(TAG, "Second pass " + win
+ " mHaveFrame=" + win.mHaveFrame
+ " mViewVisibility=" + win.mViewVisibility
+ " mRelayoutCalled=" + win.mRelayoutCalled);
if ((win.mViewVisibility != View.GONE && win.mRelayoutCalled)
|| !win.mHaveFrame) {
mPolicy.layoutWindowLw(win, win.mAttrs, win.mAttachedWindow);
win.mLayoutSeq = seq;
if (DEBUG_LAYOUT) Slog.v(TAG, "-> mFrame="
+ win.mFrame + " mContainingFrame="
+ win.mContainingFrame + " mDisplayFrame="
+ win.mDisplayFrame);
}
}
}
// Window frames may have changed. Tell the input dispatcher about it.
mInputMonitor.updateInputWindowsLw();
//调用PhoneWindowManager.finishLayoutLw()方法完成一些清理工作
return mPolicy.finishLayoutLw();
}
}在介绍该方法的实现之前,我们先了解下WindowMangerService两个成员变量:
WindowManagerPolicy mPolicy:WindowManagerPolicy是一个窗口管理策略类,它通过PolicyManager.makeNewWindow
Manager()方法创建,在Phone平台的实现类是PhoneWindowManager,它主要用来制定窗口大小的计算策略。
ArrayList<WindowState> mWindows:WindowState的列表,该列表保存了系统中的所有窗口,这些窗口按照Z轴的位置从小
到大排列在这个列表中。WindowState用来描述窗口的各种信息。该函数的执行流程主要分为3个阶段:
1 调用PhoneWindowManager.beginLayoutLw()来设置屏幕大小
2 调用PhoneWindowManager.layoutWindowLw()来计算各个窗口的大小、内容边距以及可见边距大小
3 调用PhoneWindowManager.finishLayoutLw()来执行一些清理工作我们继续来看这三个函数的执行过程。
5.1 PhoneWindowManager.beginLayoutLw(int displayWidth, int displayHeight)
public class PhoneWindowManager implements WindowManagerPolicy {
//用来描述系统状态栏窗口
WindowState mStatusBar = null;
//当前屏幕的宽度与高度
// The current size of the screen.
int mW, mH;
//描述可见区域的位置(四个坐标)
// During layout, the current screen borders with all outer decoration
// (status bar, input method dock) accounted for.
int mCurLeft, mCurTop, mCurRight, mCurBottom;
//描述内容区域的位置(四个坐标)
// During layout, the frame in which content should be displayed
// to the user, accounting for all screen decoration except for any
// space they deem as available for other content. This is usually
// the same as mCur*, but may be larger if the screen decor has supplied
// content insets.
int mContentLeft, mContentTop, mContentRight, mContentBottom;
//描述输入法所在的位置(四个坐标)
// During layout, the current screen borders along with input method
// windows are placed.
int mDockLeft, mDockTop, mDockRight, mDockBottom;
//描述输入法窗口所在Z轴的位置
// During layout, the layer at which the doc window is placed.
int mDockLayer;
//它们是一组临时的Rect区域,用来作为参数传递给具体的窗口计算大小的,避免每次都创建一组
//新的Rect区域做作为参数传递给窗口
static final Rect mTmpParentFrame = new Rect();
static final Rect mTmpDisplayFrame = new Rect();
static final Rect mTmpContentFrame = new Rect();
static final Rect mTmpVisibleFrame = new Rect();
public void beginLayoutLw(int displayWidth, int displayHeight) {
//1 初始化变量,设置mDockRight = mContentRight = mCurRight等于屏幕宽度
//设置mDockBottom = mContentBottom = mCurBottom 为屏幕高度,设置mDockLayer
//为0x10000000,这使得输入法的层级非常大,这样它就可以存在于所有窗口之上。
mW = displayWidth;
mH = displayHeight;
mDockLeft = mContentLeft = mCurLeft = 0;
mDockTop = mContentTop = mCurTop = 0;
mDockRight = mContentRight = mCurRight = displayWidth;
mDockBottom = mContentBottom = mCurBottom = displayHeight;
mDockLayer = 0x10000000;
// decide where the status bar goes ahead of time
if (mStatusBar != null) {
final Rect pf = mTmpParentFrame;
final Rect df = mTmpDisplayFrame;
final Rect vf = mTmpVisibleFrame;
pf.left = df.left = vf.left = 0;
pf.top = df.top = vf.top = 0;
pf.right = df.right = vf.right = displayWidth;
pf.bottom = df.bottom = vf.bottom = displayHeight;
//2 计算状态栏的大小,如果状态栏可见,则将mDockTop = mContentTop = mCurTop限制为
//剔除状态栏区域之后得到的屏幕区域
mStatusBar.computeFrameLw(pf, df, vf, vf);
if (mStatusBar.isVisibleLw()) {
// If the status bar is hidden, we don't want to cause
// windows behind it to scroll.
mDockTop = mContentTop = mCurTop = mStatusBar.getFrameLw().bottom;
if (DEBUG_LAYOUT) Log.v(TAG, "Status bar: mDockBottom="
+ mDockBottom + " mContentBottom="
+ mContentBottom + " mCurBottom=" + mCurBottom);
}
}
}
}该方法主要是做了些准备工作,首先我们要理解一下关键的成员变量。
int mW, mH; //当前屏幕的宽度与高度
int mCurLeft, mCurTop, mCurRight, mCurBottom;//描述可见区域的位置(四个坐标)
int mContentLeft, mContentTop, mContentRight, mContentBottom;//描述内容区域的位置(四个坐标)
int mDockLeft, mDockTop, mDockRight, mDockBottom;//描述输入法所在的位置(四个坐标)
int mDockLayer;//描述输入法窗口所在Z轴的位置 这个方法主要做了2件事情:
1 初始化变量,设置mDockRight = mContentRight = mCurRight等于屏幕宽度设置mDockBottom = mContentBottom =
mCurBottom 为屏幕高度,设置mDockLayer为0x10000000,这使得输入法的层级非常大,这样它就可以存在于所有窗口之上。
2 计算状态栏的大小,如果状态栏可见,则将mDockTop = mContentTop = mCurTop限制为剔除状态栏区域之后得到的屏幕区域。5.2 PhoneWindowManager.layoutWindowLw(WindowState win, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs, WindowState attached)
public class PhoneWindowManager implements WindowManagerPolicy {
public void layoutWindowLw(WindowState win, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs,
WindowState attached) {
// we've already done the status bar
if (win == mStatusBar) {
return;
}
if (false) {
if ("com.google.android.youtube".equals(attrs.packageName)
&& attrs.type == WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_APPLICATION_PANEL) {
Log.i(TAG, "GOTCHA!");
}
}
final int fl = attrs.flags;
final int sim = attrs.softInputMode;
//父窗口大小
final Rect pf = mTmpParentFrame;
//屏幕大小
final Rect df = mTmpDisplayFrame;
//内容区域大小
final Rect cf = mTmpContentFrame;
//可见区域大小
final Rect vf = mTmpVisibleFrame;
//如果是输入法窗口,则pf,df,cf,vf这四个区域都等于前面定义的输入法窗口大小mDoc*
if (attrs.type == TYPE_INPUT_METHOD) {
pf.left = df.left = cf.left = vf.left = mDockLeft;
pf.top = df.top = cf.top = vf.top = mDockTop;
pf.right = df.right = cf.right = vf.right = mDockRight;
pf.bottom = df.bottom = cf.bottom = vf.bottom = mDockBottom;
// IM dock windows always go to the bottom of the screen.
attrs.gravity = Gravity.BOTTOM;
mDockLayer = win.getSurfaceLayer();
} else {
//如果是非全屏Activity窗口
if ((fl &
(FLAG_LAYOUT_IN_SCREEN | FLAG_FULLSCREEN | FLAG_LAYOUT_INSET_DECOR))
== (FLAG_LAYOUT_IN_SCREEN | FLAG_LAYOUT_INSET_DECOR)) {
// This is the case for a normal activity window: we want it
// to cover all of the screen space, and it can take care of
// moving its contents to account for screen decorations that
// intrude into that space.
//具有父窗口
if (attached != null) {
// If this window is attached to another, our display
// frame is the same as the one we are attached to.
setAttachedWindowFrames(win, fl, sim, attached, true, pf, df, cf, vf);
}
//没有父窗口
else {
//1 父窗口大小会被设置为屏幕大小
pf.left = df.left = 0;
pf.top = df.top = 0;
pf.right = df.right = mW;
pf.bottom = df.bottom = mH;
//根据Activity里设置的输入法模式来设置内容边距
if ((sim & SOFT_INPUT_MASK_ADJUST) != SOFT_INPUT_ADJUST_RESIZE) {
//如果是SOFT_INPUT_MASK_ADJUST模式则说明在弹出输入法窗口时,win的窗口
//不需要重新排布,此时win的内容区域大小等于mDock*。
cf.left = mDockLeft;
cf.top = mDockTop;
cf.right = mDockRight;
cf.bottom = mDockBottom;
} else {
//如果是SOFT_INPUT_ADJUST_RESIZE模式,则说明弹出输入法窗口时,布局要重新
//排布,此时win的内容区域大小等于mContent*
cf.left = mContentLeft;
cf.top = mContentTop;
cf.right = mContentRight;
cf.bottom = mContentBottom;
}
//3 设置可见区域大小
vf.left = mCurLeft;
vf.top = mCurTop;
vf.right = mCurRight;
vf.bottom = mCurBottom;
}
} else if ((fl & FLAG_LAYOUT_IN_SCREEN) != 0) {
// A window that has requested to fill the entire screen just
// gets everything, period.
pf.left = df.left = cf.left = 0;
pf.top = df.top = cf.top = 0;
pf.right = df.right = cf.right = mW;
pf.bottom = df.bottom = cf.bottom = mH;
vf.left = mCurLeft;
vf.top = mCurTop;
vf.right = mCurRight;
vf.bottom = mCurBottom;
} else if (attached != null) {
// A child window should be placed inside of the same visible
// frame that its parent had.
setAttachedWindowFrames(win, fl, sim, attached, false, pf, df, cf, vf);
} else {
// Otherwise, a normal window must be placed inside the content
// of all screen decorations.
pf.left = mContentLeft;
pf.top = mContentTop;
pf.right = mContentRight;
pf.bottom = mContentBottom;
if ((sim & SOFT_INPUT_MASK_ADJUST) != SOFT_INPUT_ADJUST_RESIZE) {
df.left = cf.left = mDockLeft;
df.top = cf.top = mDockTop;
df.right = cf.right = mDockRight;
df.bottom = cf.bottom = mDockBottom;
} else {
df.left = cf.left = mContentLeft;
df.top = cf.top = mContentTop;
df.right = cf.right = mContentRight;
df.bottom = cf.bottom = mContentBottom;
}
vf.left = mCurLeft;
vf.top = mCurTop;
vf.right = mCurRight;
vf.bottom = mCurBottom;
}
}
if ((fl & FLAG_LAYOUT_NO_LIMITS) != 0) {
df.left = df.top = cf.left = cf.top = vf.left = vf.top = -10000;
df.right = df.bottom = cf.right = cf.bottom = vf.right = vf.bottom = 10000;
}
if (DEBUG_LAYOUT) Log.v(TAG, "Compute frame " + attrs.getTitle()
+ ": sim=#" + Integer.toHexString(sim)
+ " pf=" + pf.toShortString() + " df=" + df.toShortString()
+ " cf=" + cf.toShortString() + " vf=" + vf.toShortString());
if (false) {
if ("com.google.android.youtube".equals(attrs.packageName)
&& attrs.type == WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_APPLICATION_PANEL) {
if (true || localLOGV) Log.v(TAG, "Computing frame of " + win +
": sim=#" + Integer.toHexString(sim)
+ " pf=" + pf.toShortString() + " df=" + df.toShortString()
+ " cf=" + cf.toShortString() + " vf=" + vf.toShortString());
}
}
//计算窗口大小
win.computeFrameLw(pf, df, cf, vf);
//如果是输入法窗口,且指定了额外的内容边距与可见变量,则调整mContentBottom与mCurBottom的值
// Dock windows carve out the bottom of the screen, so normal windows
// can't appear underneath them.
if (attrs.type == TYPE_INPUT_METHOD && !win.getGivenInsetsPendingLw()) {
int top = win.getContentFrameLw().top;
top += win.getGivenContentInsetsLw().top;
if (mContentBottom > top) {
mContentBottom = top;
}
top = win.getVisibleFrameLw().top;
top += win.getGivenVisibleInsetsLw().top;
if (mCurBottom > top) {
mCurBottom = top;
}
if (DEBUG_LAYOUT) Log.v(TAG, "Input method: mDockBottom="
+ mDockBottom + " mContentBottom="
+ mContentBottom + " mCurBottom=" + mCurBottom);
}
}
}终于走到了我们最为核心的函数,该函数就是用来计算窗口的大小,窗口按照从属关系可以分为父窗口与子窗口,判断标准取决于WindowState.mLayoutAttached 的值:
- WindowState.mLayoutAttached = false :父窗口
- WindowState.mLayoutAttached = true :子窗口
子窗口的计算是依赖于父窗口的,有父窗口的会先计算父窗口,再计算子窗口,具体说来:
1 先计算父窗口的大小,一般来说,能作为父窗口的一般是Activity窗口(该类窗口的WindowState对象里的mAppToken执行一个AppWindowToken
对象,该对象用来描述一个Activity,它与ActivityRecord对应。),但是父窗口只有在以下2种情况下才会去计算大小:
(1) 窗口是可见的,窗口在以下情况时不可见:
① 窗口本身是不可见的,即WindowState.mViewVisibility = View.GONE
② 窗口本身处于退出状态,即WindowState.mExiting = true
③ 窗口本身处于正在销毁状态,即WindowState.mDestorying = true
④ 它的父窗口处于不可见状态,即WindowState.mAttachedHidden = true
⑤ 它所在窗口树的根窗口处于不可见状态,即WindowState.mRootToken.hidden = true
⑥ 它所属的Activity处于不可见状态,即WindowState.mAppToken.hiddenRequested = true
(2) 窗口还没有计算过大小。即WindowState.mHaveFrame = false
2 然后计算子窗口的大小,在计算父窗口大小的过程中,会记录位于系统最上面的一个字窗口在mWindows(ArrayList)中的位置topAttached,接下来
从这个位置开始依次向下计算每一个子窗口的大小。一个子窗口在以下两种情况下,才会被计算大小:
(1) 窗口本身是可见的,即WindowState != View.GONE
(2) 窗口还没有计算过大小。即WindowState.mHaveFrame = false
我们先来看看该函数的参数:
indowState win:当前要计算的窗口
WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs:当前要计算窗口的参数
WindowState attached:当前窗口的父窗口该函数片段主要做了以下事情:
1 计算四组值,不同情况下值的计算方式不同,具体可参见代码注释。
//父窗口大小
final Rect pf = mTmpParentFrame;
//屏幕大小
final Rect df = mTmpDisplayFrame;
//内容区域大小
final Rect cf = mTmpContentFrame;
//可见区域大小
final Rect vf = mTmpVisibleFrame;
2 根据上面计算的值,调用WindowState.computeFrameLw()计算窗口大小。
我们在接着来看WindowState.computeFrameLw()的实现。
5.3 WindowState.computeFrameLw(Rect pf, Rect df, Rect cf, Rect vf)
public class WindowManagerService extends IWindowManager.Stub
implements Watchdog.Monitor {
private final class WindowState implements WindowManagerPolicy.WindowState {
public void computeFrameLw(Rect pf, Rect df, Rect cf, Rect vf) {
//用来描述窗口大小是否已经计算过了
mHaveFrame = true;
//mContainingFrame表示当前正在处理的窗口的父窗口大小
final Rect container = mContainingFrame;
container.set(pf);
//mContainingFrame表示当前正在处理的窗口的屏幕大小
final Rect display = mDisplayFrame;
display.set(df);
//兼容模式
if ((mAttrs.flags & FLAG_COMPATIBLE_WINDOW) != 0) {
container.intersect(mCompatibleScreenFrame);
if ((mAttrs.flags & FLAG_LAYOUT_NO_LIMITS) == 0) {
display.intersect(mCompatibleScreenFrame);
}
}
final int pw = container.right - container.left;
final int ph = container.bottom - container.top;
//1 计算内容区域的宽高
int w,h;
if ((mAttrs.flags & mAttrs.FLAG_SCALED) != 0) {
w = mAttrs.width < 0 ? pw : mAttrs.width;
h = mAttrs.height< 0 ? ph : mAttrs.height;
} else {
//是否指定了窗口大小等于父窗口大小,如果等于则设置为pw与ph描述的宽度与高度
//如果不等于则设置为WIndowManagerService所所设置的大小,即mRequestedWidth与mRequestedHeight
w = mAttrs.width == mAttrs.MATCH_PARENT ? pw : mRequestedWidth与;
h = mAttrs.height== mAttrs.MATCH_PARENT ? ph : mRequestedHeight;
}
final Rect content = mContentFrame;
content.set(cf);
final Rect visible = mVisibleFrame;
visible.set(vf);
final Rect frame = mFrame;
final int fw = frame.width();
final int fh = frame.height();
//System.out.println("In: w=" + w + " h=" + h + " container=" +
// container + " x=" + mAttrs.x + " y=" + mAttrs.y);
//根据窗口的gravity值,位置,初始大小以及窗口大小来计算窗口大小,并保存在frame变量中。
Gravity.apply(mAttrs.gravity, w, h, container,
(int) (mAttrs.x + mAttrs.horizontalMargin * pw),
(int) (mAttrs.y + mAttrs.verticalMargin * ph), frame);
//System.out.println("Out: " + mFrame);
//前面计算的窗口大小没有考虑屏幕大小,这里调用Gravity.applyDisplay()方法将前面计算得到
//的窗口限制在屏幕区域中。即限制咋WindowState.mDisplayFrame所描述的区域中。
// Now make sure the window fits in the overall display.
Gravity.applyDisplay(mAttrs.gravity, df, frame);
//保证窗口的内容区域与可见区域包含在整个窗口区域中
// Make sure the content and visible frames are inside of the
// final window frame.
if (content.left < frame.left) content.left = frame.left;
if (content.top < frame.top) content.top = frame.top;
if (content.right > frame.right) content.right = frame.right;
if (content.bottom > frame.bottom) content.bottom = frame.bottom;
if (visible.left < frame.left) visible.left = frame.left;
if (visible.top < frame.top) visible.top = frame.top;
if (visible.right > frame.right) visible.right = frame.right;
if (visible.bottom > frame.bottom) visible.bottom = frame.bottom;
//2 计算内容边距
final Rect contentInsets = mContentInsets;
contentInsets.left = content.left-frame.left;
contentInsets.top = content.top-frame.top;
contentInsets.right = frame.right-content.right;
contentInsets.bottom = frame.bottom-content.bottom;
//3 计算可见边距
final Rect visibleInsets = mVisibleInsets;
visibleInsets.left = visible.left-frame.left;
visibleInsets.top = visible.top-frame.top;
visibleInsets.right = frame.right-visible.right;
visibleInsets.bottom = frame.bottom-visible.bottom;
if (mIsWallpaper && (fw != frame.width() || fh != frame.height())) {
updateWallpaperOffsetLocked(this, mDisplay.getWidth(),
mDisplay.getHeight(), false);
}
if (localLOGV) {
//if ("com.google.android.youtube".equals(mAttrs.packageName)
// && mAttrs.type == WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_APPLICATION_PANEL) {
Slog.v(TAG, "Resolving (mRequestedWidth="
+ mRequestedWidth + ", mRequestedheight="
+ mRequestedHeight + ") to" + " (pw=" + pw + ", ph=" + ph
+ "): frame=" + mFrame.toShortString()
+ " ci=" + contentInsets.toShortString()
+ " vi=" + visibleInsets.toShortString());
//}
}
}
}
}该函数主要做了以下事情:
1 计算内容区域的宽高,根据窗口的gravity值,位置,初始大小以及窗口大小调用Gravity.apply()方法计算窗口大小,并保存在
frame变量中。
2 计算内容边距
3 计算可见边距5.4 PhoneWindowManager.finishLayoutLw()
public class PhoneWindowManager implements WindowManagerPolicy {
public int finishLayoutLw() {
return 0;
}
}最后一步调用finishLayoutLw()函数,该函数是个空实现,它什么也不做。
二 窗口位置的计算
前面我们分析了窗口大小的计算流程,也就是X/Y轴的计算,我们知道在Android系统中,无论是普通的Activity窗口,输入法窗口还是壁纸窗口都是被WindowManagerService组织在一个堆栈里 ,它们在堆栈里的位置就代表了它们在Z轴的位置,Z轴位置大的排列在Z轴位置小的上面。
关于z-order
手机屏幕是以左上角为原点,向右为X轴方向,向下为Y轴方向的一个二维空间。为了方便管理窗口的显示次序,手机的屏幕被扩展为了 一个三维的空间,即多定义了 一个Z轴,其方向为垂直于屏幕表面指向屏幕外。多个窗口依照其前后顺序排布在这个虚拟的Z轴上,因此 窗口的显示次序又被称为Z序(Z order)。
一个Window的次序有两个参数决定:
int mBaseLayer:用于描述窗口及其子窗口在所有窗口中的显示位置,主序越大,则窗口及其子窗口的显示位置相对于其他窗口的位置越靠前。
int mSubLayer:描述了一个子窗口在其兄弟窗口中的显示位置,子序越大,则子窗口相对于其兄弟窗口的位置越靠前。窗口的主序表
| 窗口类型 | 主序 |
|---|---|
| TYPE_UNIVERSE_BACKGROUND | 11000 |
| TYPE_WALLPAPER | 21000 |
| TYPE_PHONE | 31000 |
| TYPE_SEARCH_BAR | 41000 |
| TYPE_RECENTS_OVERLAY | 51000 |
| TYPE_SYSTEM_DIALOG | 51000 |
| TYPE_TOAST | 61000 |
| TYPE_PRIORITY_PHONE | 71000 |
| TYPE_DREAM | 81000 |
| TYPE_SYSTEM_ALERT | 91000 |
| TYPE_INPUT_METHOD | 101000 |
| TYPE_INPUT_METHOD_DIALOG | 111000 |
| TYPE_KEYGUARD | 121000 |
| TYPE_KEYGUARD_DIALOG | 131000 |
| TYPE_STATUS_BAR_SUB_PANEL | 141000 |
| 应用窗口与未知类型的窗口 | 21000 |
窗口的子序表
| 子窗口类型 | 子序 |
|---|---|
| TYPE_APPLICATION_PANEL | 1 |
| TYPE_APPLICATION_ATTACHED_DIALOG | 1 |
| TYPE_APPLICATION_MEDIA | -2 |
| TYPE_APPLICATION_MEDIA_OVERLAY | -1 |
| TYPE_APPLICATION_SUB_PANEL | 2 |
窗口在Z轴上的位置受窗口类型,创建顺序和运行状态有关,Z轴位置的计算主要发生在以下两个场景:
- 应用请求WindowManagerService增加一个窗口
- 应用请求WindowManagerService重新布局一个窗口
在文章04Android显示框架:Activity应用视图的创建流程 中,我们就提到,应用请求增加一个窗口,最终会调用WindowManagerService.addWindow()方法。
关键点1:WindowManagerService.addWindow()
public class WindowManagerService extends IWindowManager.Stub
implements Watchdog.Monitor {
......
public int addWindow(Session session, IWindow client,
WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs, int viewVisibility,
Rect outContentInsets, InputChannel outInputChannel) {
......
synchronized(mWindowMap) {
......
WindowToken token = mTokenMap.get(attrs.token);
......
win = new WindowState(session, client, token,
attachedWindow, attrs, viewVisibility);
......
if (attrs.type == TYPE_INPUT_METHOD) {
mInputMethodWindow = win;
addInputMethodWindowToListLocked(win);
......
} else if (attrs.type == TYPE_INPUT_METHOD_DIALOG) {
mInputMethodDialogs.add(win);
addWindowToListInOrderLocked(win, true);
adjustInputMethodDialogsLocked();
......
} else {
addWindowToListInOrderLocked(win, true);
if (attrs.type == TYPE_WALLPAPER) {
......
adjustWallpaperWindowsLocked();
} else if ((attrs.flags&FLAG_SHOW_WALLPAPER) != 0) {
adjustWallpaperWindowsLocked();
}
}
......
assignLayersLocked();
......
}
......
}
......
} 这个方法我们只关注窗口Z轴位置计算的部分,从方法中我们可以看出,不同的窗口类型,计算方式是不一样的,具体说来:
- 如果添加的是一个输入法窗口,那么就调用成员函数addInputMethodWindowToListLocked将它放置在需要显示输入法的窗口的上面去;
- 如果添加的是一个输入法对话框,那么就先调用成员函数addWindowToListInOrderLocked来将它插入到窗口堆栈中,接着再调用成员函数adjustInputMethodDialogsLocked来将它放置在输入法窗口的上面;
- 如果添加的是一个普通窗口,那么就直接调用成员函数addWindowToListInOrderLocked来将它插入到窗口堆栈中;
- 如果添加的是一个普通窗口,并且这个窗口需要显示壁纸,那么就先调用成员函数addWindowToListInOrderLocked来将它插入到窗口堆栈中,接着再调用成员函数adjustWallpaperWindowsLocked来将壁纸窗口放置在它的下面。
- 如果添加的是一个壁纸窗口,那么就先调用成员函数addWindowToListInOrderLocked来将它插入到窗口堆栈中,接着再调用成员函数adjustWallpaperWindowsLocked来将它放置在需要显示壁纸的窗口的下面。
不管是哪种类型,最终都会调用WindowManagerService.assignLayersLocked()来重新计算系统中所有窗口的Z轴位置,这是因为前面往窗口堆栈增加了一个新的窗口。
关键点2:WindowManagerService.assignLayersLocked()
我们前面说过,一个Window的次序有两个参数决定:
int mBaseLayer:用于描述窗口及其子窗口在所有窗口中的显示位置,主序越大,则窗口及其子窗口的显示位置相对于其他窗口的位置越靠前。
int mSubLayer:描述了一个子窗口在其兄弟窗口中的显示位置,子序越大,则子窗口相对于其兄弟窗口的位置越靠前。这两个变量都保存在WindowStat对象中,在创建WindowState对象时,即调用它的构造方法时,会计算这两个值
mBaseLayer = mPolicy.windowTypeToLayerLw(attachedWindow.mAttrs.type) * TYPE_LAYER_MULTIPLIER+ TYPE_LAYER_OFFSET;
mSubLayer = mPolicy.subWindowTypeToLayerLw(a.type);注:可以看到windowTypeToLayerLw()方法的返回值并没有直接被使用,而是* TYPE_LAYER_MULTIPLIER+ TYPE_LAYER_OFFSET,这是因为在Android系统中相同类型的Z轴位于 相同的值域,不同类型的窗口则处于两个不相交的值域,又由于每一种类型地窗口的数量是不确定的,所以需要预留一个范围足够大的值域来满足需求。
PhoneWindowManager.windowTypeToLayerLw()与PhoneWindowManager.subWindowTypeToLayerLw()该方法正如它的名字那样,将窗口type转换成对应的layer。
主序
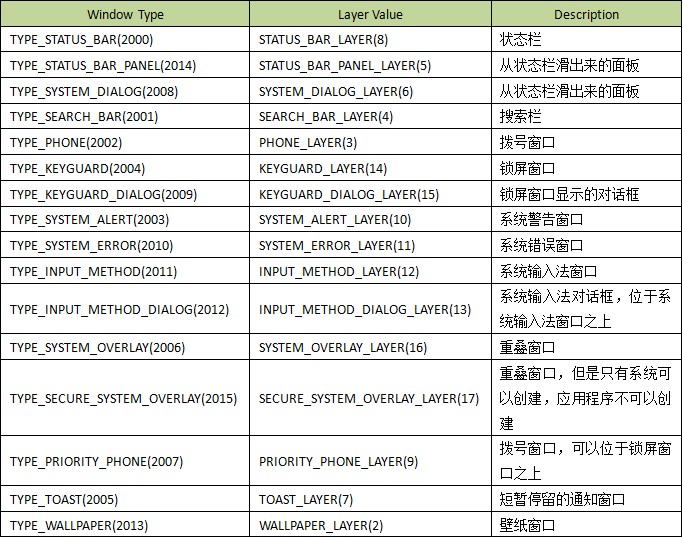
次序

public class WindowManagerService extends IWindowManager.Stub
implements Watchdog.Monitor {
private final void assignLayersLocked() {
int N = mWindows.size();
int curBaseLayer = 0;
int curLayer = 0;
int i;
for (i=0; i<N; i++) {
WindowState w = mWindows.get(i);
if (w.mBaseLayer == curBaseLayer || w.mIsImWindow
|| (i > 0 && w.mIsWallpaper)) {
curLayer += WINDOW_LAYER_MULTIPLIER;
w.mLayer = curLayer;
} else {
curBaseLayer = curLayer = w.mBaseLayer;
w.mLayer = curLayer;
}
if (w.mTargetAppToken != null) {
w.mAnimLayer = w.mLayer + w.mTargetAppToken.animLayerAdjustment;
} else if (w.mAppToken != null) {
w.mAnimLayer = w.mLayer + w.mAppToken.animLayerAdjustment;
} else {
w.mAnimLayer = w.mLayer;
}
if (w.mIsImWindow) {
w.mAnimLayer += mInputMethodAnimLayerAdjustment;
} else if (w.mIsWallpaper) {
w.mAnimLayer += mWallpaperAnimLayerAdjustment;
}
if (DEBUG_LAYERS) Slog.v(TAG, "Assign layer " + w + ": "
+ w.mAnimLayer);
//System.out.println(
// "Assigned layer " + curLayer + " to " + w.mClient.asBinder());
}
}
}在调用该方法之前,系统中所有窗口在窗口堆栈中的位置都已经排列好了,该函数从下往上遍历窗口堆栈,以连续排列在一起类型相同的窗口为单位来计算每个周口的Z轴位置。
- 每次遇到一个窗口,它的BaseLayer值与上一次计算的窗口的BaseLayer值不相等,就开始一个新的计算单元。
- 在每一个计算单元中,第一个窗口的Z轴位置就等于它的BaseLayer值,而之后的每一个窗口的Z轴位置都比前一个窗口的Z轴位置大WINDOW_LAYER_MULTIPLIER。
至此,WindowManagerService服务计算窗口Z轴位置的过程就分析完成了,我们再来总结一下。
- WindowManagerService服务将窗口排列在一个窗口堆栈中。
- WindowManagerService服务根据窗口类型以及窗口在窗口堆栈的位置来计算得窗口的Z轴位置。
- WindowManagerService服务通过Java层的Surface类的成员函数setLayer来将窗口的Z轴位置设置到SurfaceFlinger服务中去。
- Java层的Surface类的成员函数setLayer又是通过调用C++层的SurfaceControl类的成员函数setLayer来将窗口的Z轴位置设置到SurfaceFlinger服务中去的。