Why are you here?
Why are you here?
-
你想要更好的理解Android是怎样工作的
。Intent、ContextProvider、Messenger
。访问系统的服务
。生命周期中的回调
。安全 - 你想要通过高效率和低延时的IPC框架打破应用程序模块化的业务逻辑
- 你想要添加新的系统服务,可以更好地暴露给开发人员
- 你只是感觉IPC和Binder是不可缺少的,有趣的
- 你没有其它的事要做啦
Objectives
- Binder Overview
- IPC
- Advantages of Binder
- Binder vs Intent/ContentProvider/Messenger-based IPC Binder Terminology
- Binder Communication and Discovery AIDL
- Binder Object Reference Mapping Binder by Example
- Async Binder Memory Sharing Binder Limitations Security
Slides and screencast from this class will be posted to: http://mrkn.co/bgnhg
Who am I?
亚历山大 加尔根塔

Developer and instructor of Android Internals and Security training at
Marakana
- 马里亚纳(位于西太平洋)Android Internals and Security training的开发者和指导师
- San Francisco Android User Group (sfandroid.org)的创始人和组织者
- San Francisco Java User Group (sfjava.org) 的创始人和组织者
- San Francisco HTML5 User Group (sfhtml5.org) 的合作发起人和组织者
- AnDevCon, AndroidOpen, Android Builders Summit 等等的演讲者
- Server-side Java and Linux, since 1997
- Android/embedded Java and Linux, since 2009
- 曾就职于 SMS, WAP Push, MMS, OTA provisioning
-
Follow
。@agargenta
。+Aleksandar Gargenta
。http://marakana.com/s/author/1/aleksandar_gargenta
What is Binder?
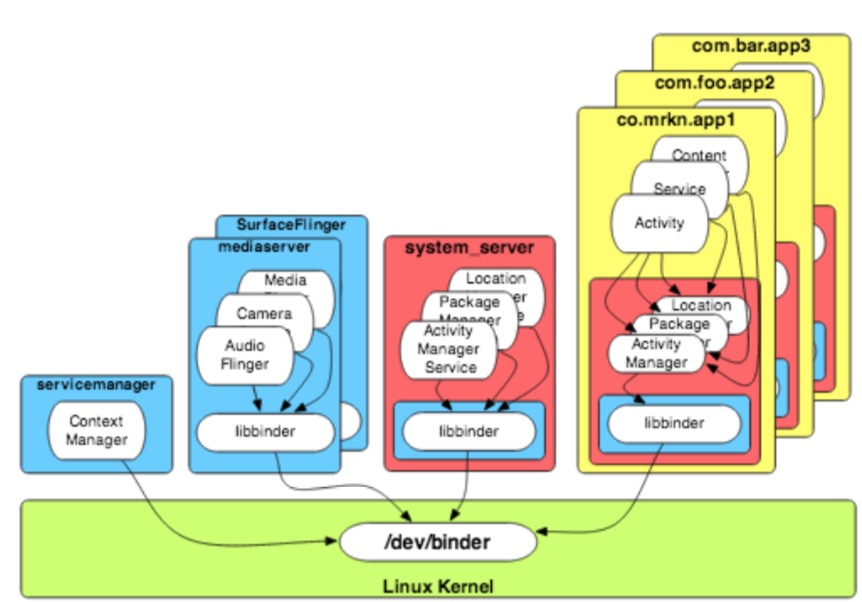
-
一个IPC组件,开发面向对象的操作系统服务
。没有另外一个面向对象内核
。代替运行在传统内核上,面向对象的操作系统环境,如:Linux - Android的关键
-
来自OpenBinder
- 发源于 Be,Inc ,作为 "next generation BeOS"(~ 2001) 的关键部分
- 被 PalmSource 收购
- 最初使用在 Palm Cobalt (micro-kernel based OS)
- Palm 切换到 Linux,所以,Binder被移植到Linux,开源(~ 2005)
- 谷歌雇用了OpenBinder的核心工程师Dianne Hackborn,加入Android团队(~ 2008)
- OpenBinder不再维护 -- Binder长存
- 专注于可伸缩性、稳定性、灵活性、低延迟和开销、简单的编程模型
Why Binder?

-
出于安全性、稳定性和内存管理的考虑,Android的应用和系统服务运行在分离的进程中,但是它们之间需要通信和共享数据
。安全性:每一个进程就是一个沙盒,运行在一个不同的系统标识中
。稳定性:如果一个进程失常(例如:崩溃),它不影响其它的进程
。内存管理:“不需要”的进程会被移除,为新的释放资源(主要是内存)
。事实上,一个单独的Android应用可以让它的组件运行在不同的进程中 -
IPC来拯救
。如果我们需要避免传统IPC开销和服务拒绝的问题
-
Android的libc(a.k.a bionic)库不支持System V IPCs
。没有SysV信号量,共享内存、消息队列等等
。当一个进程终止时,“忘记”释放IPC共享资源,System V IPC会报内存资源泄露的错误
。bug,恶意代码或者一个正常的应用在低内存的情况下都会无条件终止 -
Binder来拯救
。其内置的“对象”引用的引用计数器,加上消亡提醒机制,让它适用于“敌对的”环境(低内存强杀)
。当一个Binder服务没有任何终端引用时,它的所有者可以自动提醒它去处理自己 -
很多其它的特性:
。"线程迁移" - 如,编程模式:
- 远程对象可以像本地的一样调用自动管理线程池方法
- “跳转”到其它的进程中
- 同步和异步(单向)的调用模式
。分辨发送者和接受者(通过UID/PID)- 对于安全很重要
。独特的跨进程边界对象映射
。一个远程对象的引用可以传递到的另外的进程中,并且可以用作一个标志令牌
。各个进程之间发送文件描述符的能力
。简单的Android接口定义语言(AIDL)
。内置支持很多编组的常见数据类型
。通过自动生成的代理和存根简化事务调用模型(只有Java)
。跨进程递归 - 例如:当调用本地对象上的方法时就跟递归的语义一样
。如果客户端和服务器运行在同样的进程中,就会是本地执行模式(不是IPC数据信号编集) -
但是:
。不支持RPC(只有本地)
。客户端与服务之间是基于消息的通信 - 不适合流
。没有被POSIX或任何其他标准定义 -
大多数应用程序和核心系统服务依赖于Binder
。应用程序大多数生命周期的回调(例如:onResume(), onDestory(), etc.)会通过Binder被ActivityManagerService调用
。关闭binder,然后整个系统慢慢停止(无显示,无音频,无输入,无传感器,...)
。有些情况下使用Unix域中的socket(例如:RILD)
IPC with Intents and ContentProviders?
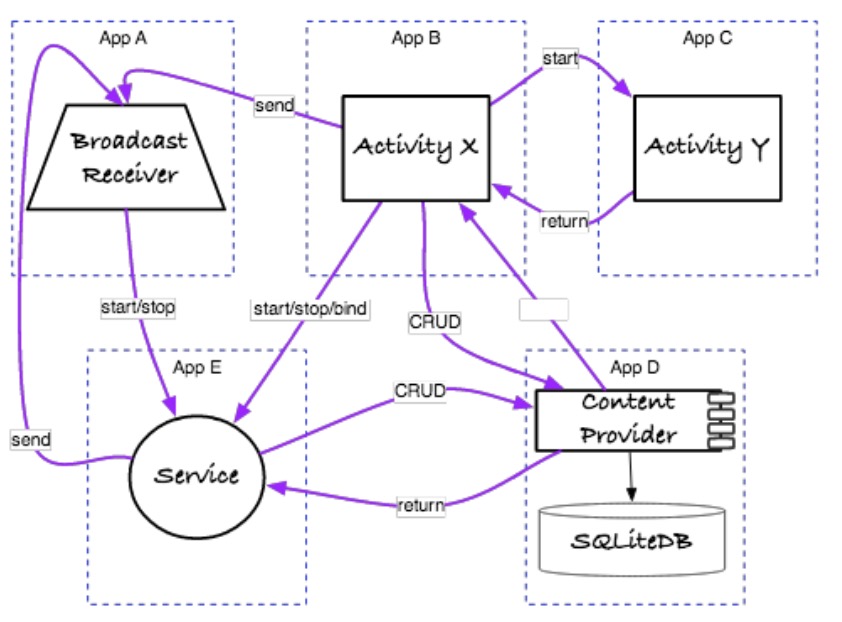
- 通过Intent和content provider Android支持一个简单形式的IPC
-
意图的消息传递是Android组件之间异步通信的一个框架
。这些组件可能运行在相同的或不同的应用中(例如:多进程)
。支持点对点和发布-订阅消息传递域
。意图本身代表一个包含操作的描述和传递给接受者的数据
。隐式意图能够给APIs解耦合 -
ContentResolver通过稳定的(CRUB)API 与 ContentProviders (典型的运行在不同的应用中的)同步通信
- 所以的Android组件都可以是发送者,但是大多数是接受者
- 所有通信发生在循环线程(又称主线程)中
-
但是:
。不是真实的面向对象
。只有基于intent的异步通信
。不适合低延时
。因为,API定义地松散,所以容易发生运行时错误
。所有的底层通信都是基于Binder的
。事实上,Intent和ContentProvider只是Binder的高级抽象
。基于系统服务方便扩展:ActivityManagerService和PackageManagerService
For example:
src/com/marakana/shopping/UpcLookupActivity.java
public class ProductLookupActivity extends Activity {
private static final int SCAN_REQ = 0; ...
public void onClick(View view) {
Intent intent = new Intent("com.google.zxing.client.android.SCAN"); //1
intent.setPackage("com.google.zxing.client.android"); //1
intent.putExtra("SCAN_MODE", "PRODUCT_MODE"); //2
super.startActivityForResult(intent, SCAN_REQ); //3
}
@Override
protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, Intent data) { //4
if (requestCode == SCAN_REQ && resultCode == RESULT_OK) { //5
String barcode = data.getStringExtra("SCAN_RESULT"); //6
String format = data.getStringExtra("SCAN_RESULT_FORMAT"); //6
...
super.startActivity(
new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW,
Uri.parse("http://www.upcdatabase.com/item/" + barcode))); //7
 }
...
}
}
src/com/google/zxing/client/android/CaptureActivity.java:
...
public class CaptureActivity extends Activity {
...
private void handleDecodeExternally(Result rawResult, ...) {
Intent intent = new Intent(getIntent().getAction());
intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_WHEN_TASK_RESET);
intent.putExtra(Intents.Scan.RESULT, rawResult.toString()); //8
intent.putExtra(Intents.Scan.RESULT_FORMAT,
rawResult.getBarcodeFormat().toString());
...
super.setResult(Activity.RESULT_OK, intent);
super.finish(); //9
}
}
- 1 指定我们要调用的是谁
- 2 为我们的调用指定输入参数
- 3 启动异步调用
- 4 通过回调接收响应
- 5 确认这是我们预期的响应
- 6 得到响应
- 7 启动另一个IPC请求,但不期望结果
- 8 在服务方面,把结果放在一个新的Intent中
- 9 异步发回结果
Messenger IPC
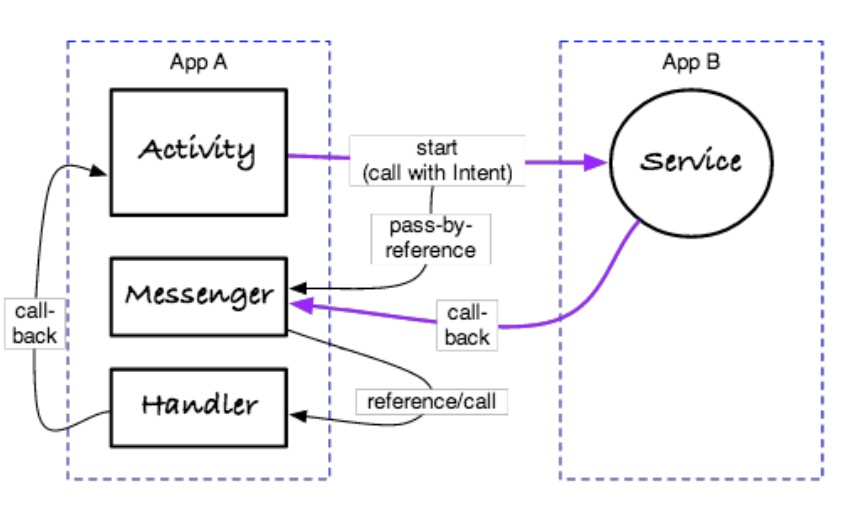
- Android的Messenger表示一个可以通过Intent发送到远程进程中的Handler引用
- Messenger的引用可以通过Intent传递,使用前面提到的IPC机制来实现
- 远程进程发送消息,通过Messenger,发送到本地的处理程序中
- Messenger就像是Intent,它们可以指定“行为”(aMessge.what)和数据(aMessage.getData())
- 仍然是异步,但却是更低的延迟/开销
- 从服务端到客户端高效的回调
- 消息默认会在循环器线程中处理
- 所有底层的通信依然基于Binder
- 例如,如何定义客户端:
src/com/marakana/android/download/client/DownloadClientActivity.java:
...
public class DownloadClientActivity extends Activity {
private static final int CALLBACK_MSG = 0;
...
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
Intent intent = new Intent( "com.marakana.android.download.service.SERVICE"); //1
ArrayList<Uri> uris = ...
intent.putExtra("uris", uris); //2
Messenger messenger = new Messenger(new ClientHandler(this)); //3
intent.putExtra("callback-messenger", messenger); //4
super.startService(intent); //5
}
private static class ClientHandler extends Handler {
private final WeakReference<DownloadClientActivity> clientRef; //6
public ClientHandler(DownloadClientActivity client) {
this.clientRef = new WeakReference<DownloadClientActivity>(client);
}
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) { //7
Bundle data = msg.getData();
DownloadClientActivity client = clientRef.get();
if (client != null && msg.what == CALLBACK_MSG && data != null) {
Uri completedUri = data.getString("completed-uri"); //8
// client now knows that completedUri is done
...
}
}
}
}
- 1 指定我们想要调用的对象(返回使用Intent)
- 2 为我们的调用指定输入参数
- 3 在我们的handler中创建一个messenger
- 4 传递的messenger也是输入的参数
- 5 启动异步的调用
- 6 我们的handler保存客户端的引用
- 7 通过一个handler中的回调收接收响应
- 8 获取响应数据
- 和我们的服务端可以看下面:
src/com/marakana/android/download/service/DownloadService.java:
...
public class MessengerDemoService extends IntentService {
private static final int CALLBACK_MSG = 0;
...
@Override
protected void onHandleIntent(Intent intent) { //1
ArrayList<Uri> uris = intent.getParcelableArrayListExtra("uris"); //2
Messenger messenger = intent.getParcelableExtra("callback-messenger"); //3
for (Uri uri : uris) {
// download the uri
...
if (messenger != null) {
Message message = Message.obtain(); //4
message.what = CALLBACK_MSG;
Bundle data = new Bundle(1);
data.putParcelable("completed-uri", uri); //5
message.setData(data); //4
try {
messenger.send(message); //6
} catch (RemoteException e) {
...
} finally {
message.recycle(); //4 }
}
}
}
}
- 1 处理客户端的请求(可能是本地的或远程的)
- 2 获取请求数据
- 3 获取messenger的引用
- 4 用Message作为数据的通用信封
- 5 设置我们的应答
- 6 发送我们的应答
Binder 术语
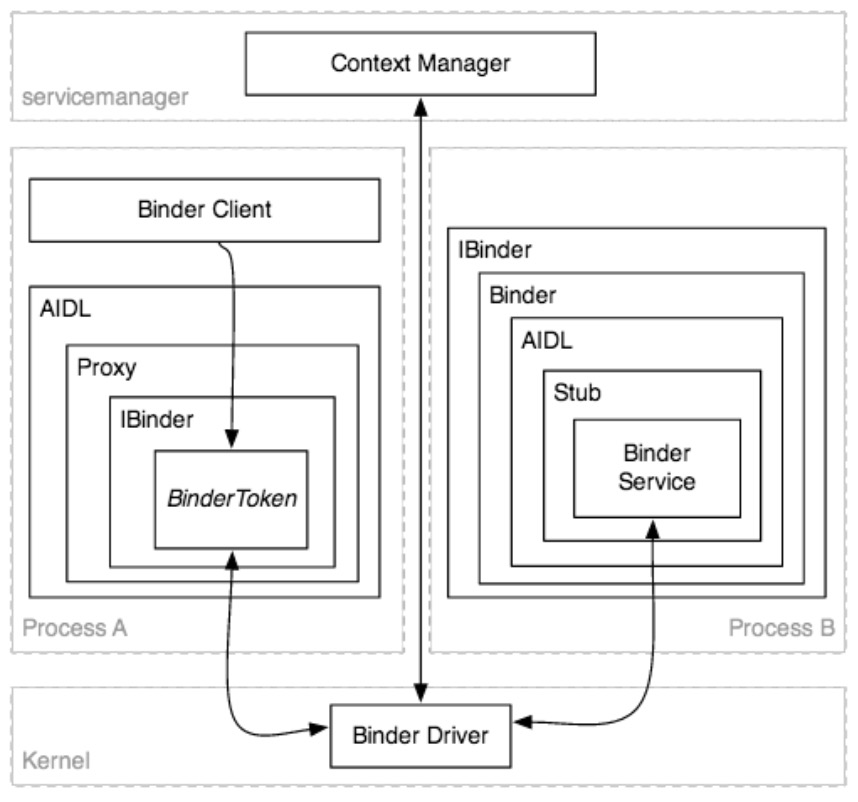
-
Binder (Framework)
所有的IPC架构 -
Binder Driver
内核级别的驱动,处理各个进程之间的通信 -
Binder Protocol
底层协议(基于ioctl),用于与Binder驱动通信 -
IBinder Interface
定义良好的行为(例如:方法),Binder对象必须实现 -
AIDL
Android接口定义语言,用于描述IBinder接口的业务操作 -
Binder (Object)
通用IBinder接口的实现 -
Binder Token
一个抽象的32位数值,在系统的所有进程中唯一的标识一个Binder对象 -
Binder Service
真正实现Binder(对象)的业务操作 -
Binder Client
一个对象,使用Binder服务提供的行为 -
Binder Transaction
远程Binder对象调用一个行为(例如:一个方法),基于Binder协议,可能涉及发送、接受的数据 -
Parcel
"可以在IBinder中发送消息的容器(数据和对象的引用)",事务处理的数据单元——一个用作流出请求,另一个用作流入响应 -
Marshalling
将高级的应用程序数据结构(例如:请求、响应参数)转化成parcel对象的过程,目的是将它们嵌套进Binder的事务中
-
Unmarshalling
将Binder事务中获取到的parcel对象重构成高级应用的数据结构的过程(例如:请求、响应参数) -
Proxy
一个AIDL接口的实现,编组、解组数据,映射调用事务的方法,将一个封装的IBinder引用指向Binder对象 -
Stub
一个AIDL接口局部的实现,当编组/解组数据时,映射事务到Binder Service调用 -
Context Manager (a.k.a. servicemanager)
一个特殊的已知处理的Binder对象,被用作为其它Binder注册、查询
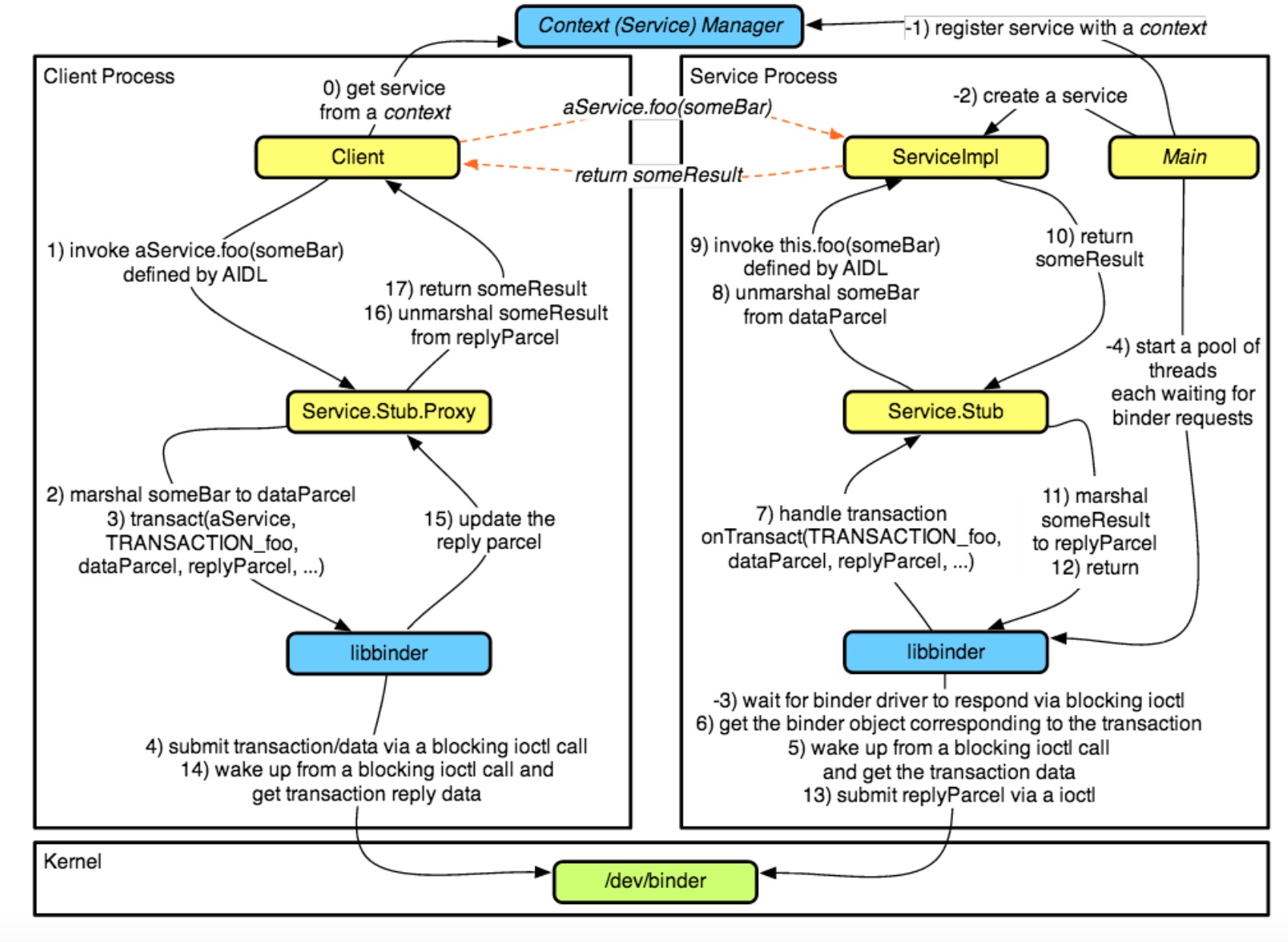
Binder Communication and Discovery
Binder通信挖掘
- 对于关注的客户端,它只是想使用服务:
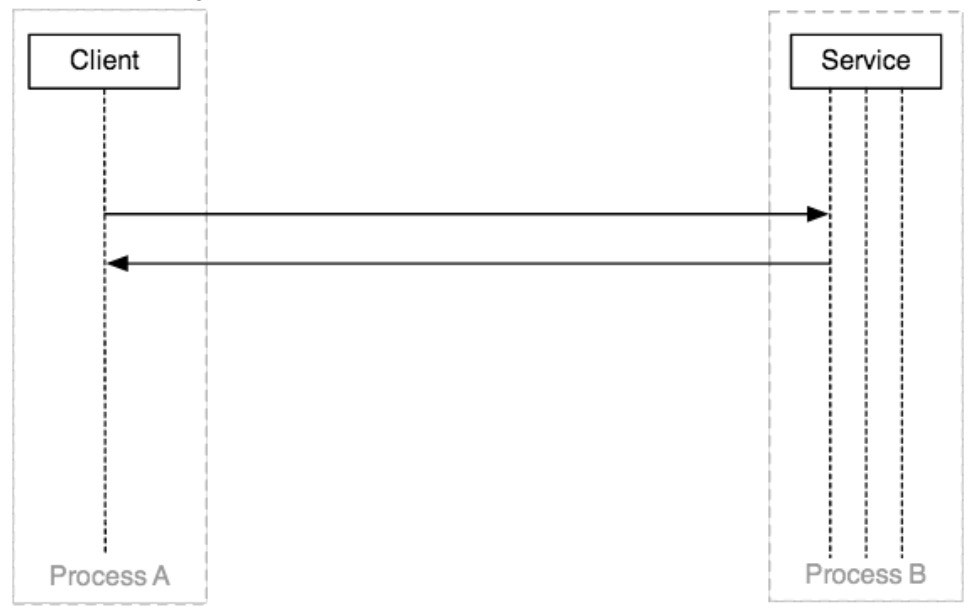
- 当进程不能直接操作其它的进程(或者读写数据),内核可以做到,因此他们使用Binder驱动:
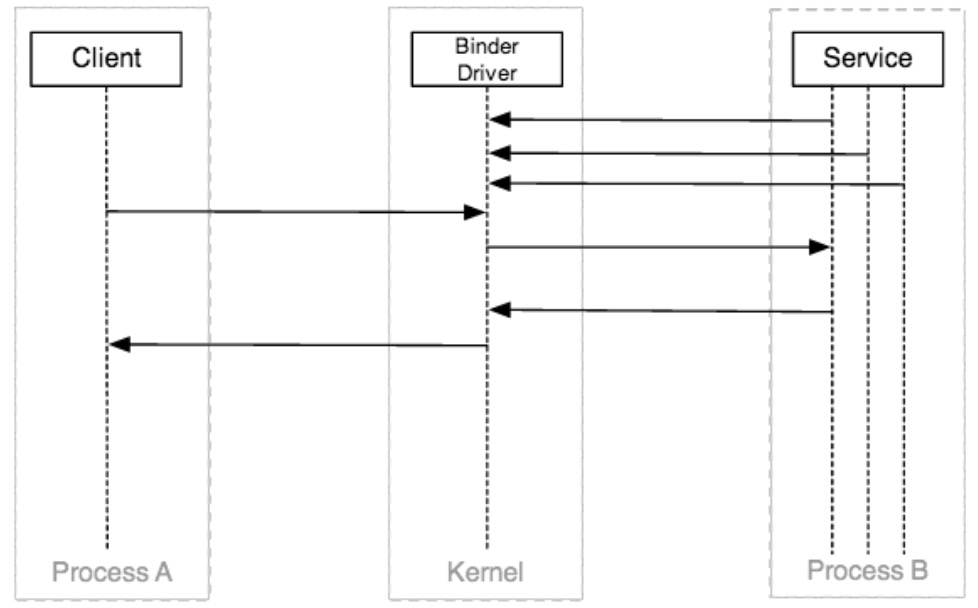
警告:因为服务端可能从多个客户端得到并发的请求,所以,它需要保护(同步访问的)其变量的状态
- Binder驱动通过/dev/binder暴露出来,并提供了相关联的基于open、release、poll、mmap、flush、ioctl的操作
- 事实上,大多数的通信都是通过ioctl(binderFd, BINDER_WRITE_READ, &bwd)进行的,bwd被定义为:
struct binder_write_read {
signed long write_size; /* bytes to write */
signed long write_consumed; /* bytes consumed by driver */
unsigned long write_buffer;
signed long read_size; /* bytes to read */
signed long read_consumed; /* bytes consumed by driver */
unsigned long read_buffer;
};
-
write_buffer包含一系列操作驱动的命令
。Book-keeping命令,例如:增加、减少binder对象的引用,请求、清除死亡通知
。请求响应的命令,例如:BC_TRANSACTION -
read_buffer包含用户操作的命令
。book-keeping命令
。操作响应的命令或执行嵌套(递归)请求处理 - 客户端通过事务与服务端通信,事务中包含一个binder token、方法体、原始缓存数据和PID/UID的发送者(驱动添加的)
- 客户端和服务端使用的大多数底层的操作和数据结构(例如:Parcel)是libbinder的抽象(在底层)
- 为了避免客户端和服务知道Binder协议和libbinder所有事情,它们使用代理和存根:
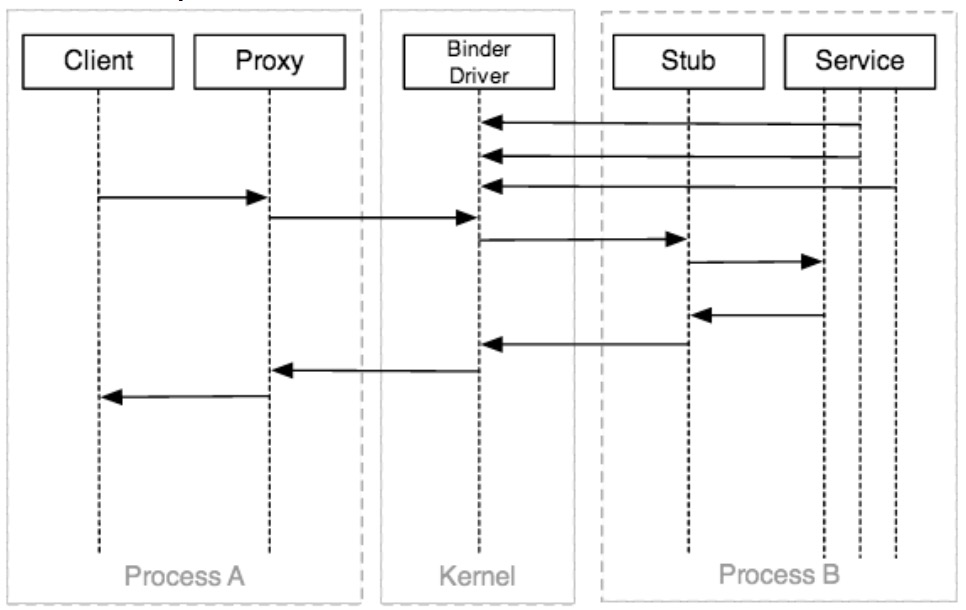
注意:基于java的代理和存根可以通过描述服务的aidl工具自动生成
- 事实上,大多数的客户端都不知道它们正在使用IPC,从来没有提过Binder或者代理,因为,它们依靠抽象来管理它们的复杂性:


注意:对系统服务来说,这是非常正确的,它们使用管理者只向客户端暴露了API的一个子集
- 但是,客户端是怎么获取到它想要会话的handle的呢?只需要问Servicemanager(Binder's CONTEXT_MGR),希望当前的服务已经注册了handle:
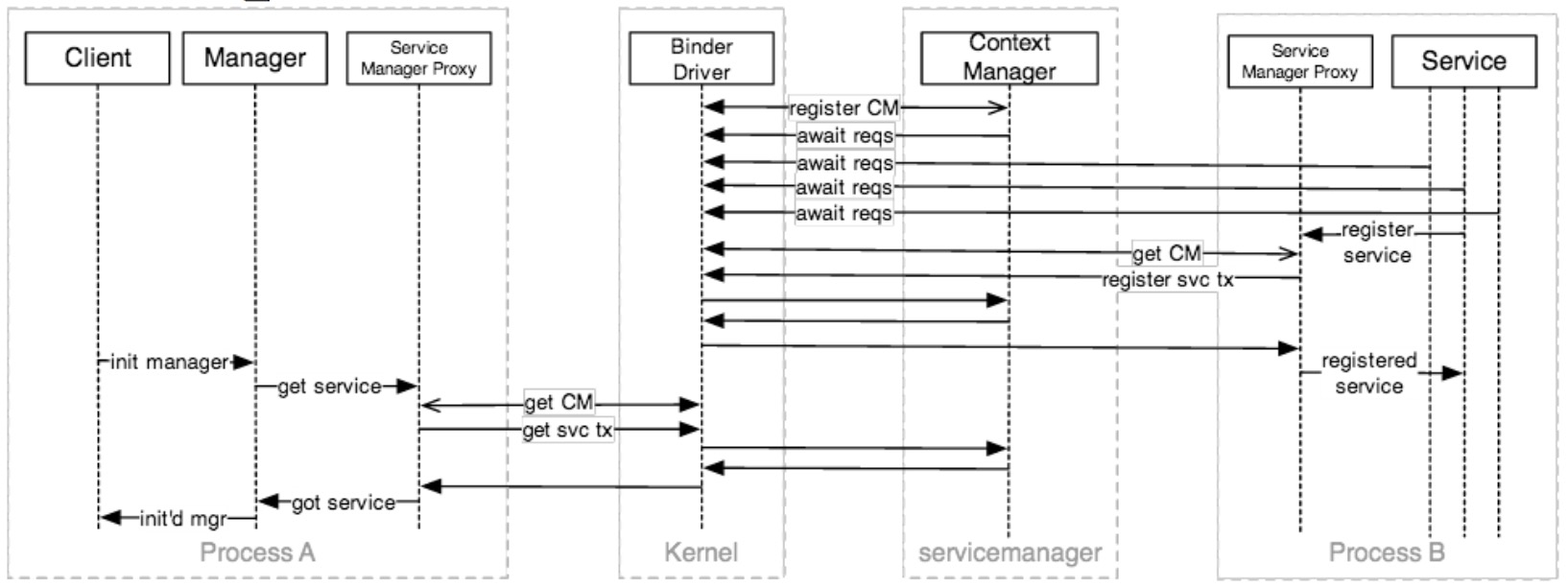
注意:出于安全、健康的原因,Binder驱动一次只会接受一个CONTEXT_MGR注册,这就是为什么Android中的Servicemanager是第一批启动的服务
- 想使用servicemanager获取当前注册的服务清单,运行:
$ adb shell service list
Found 71 services:
0 sip: [android.net.sip.ISipService]
1 phone: [com.android.internal.telephony.ITelephony]
...
20 location: [android.location.ILocationManager]
...
55 activity: [android.app.IActivityManager]
56 package: [android.content.pm.IPackageManager]
...
67 SurfaceFlinger: [android.ui.ISurfaceComposer]
68 media.camera: [android.hardware.ICameraService]
69 media.player: [android.media.IMediaPlayerService]
70 media.audio_flinger: [android.media.IAudioFlinger]
- 另外一种查看方式:
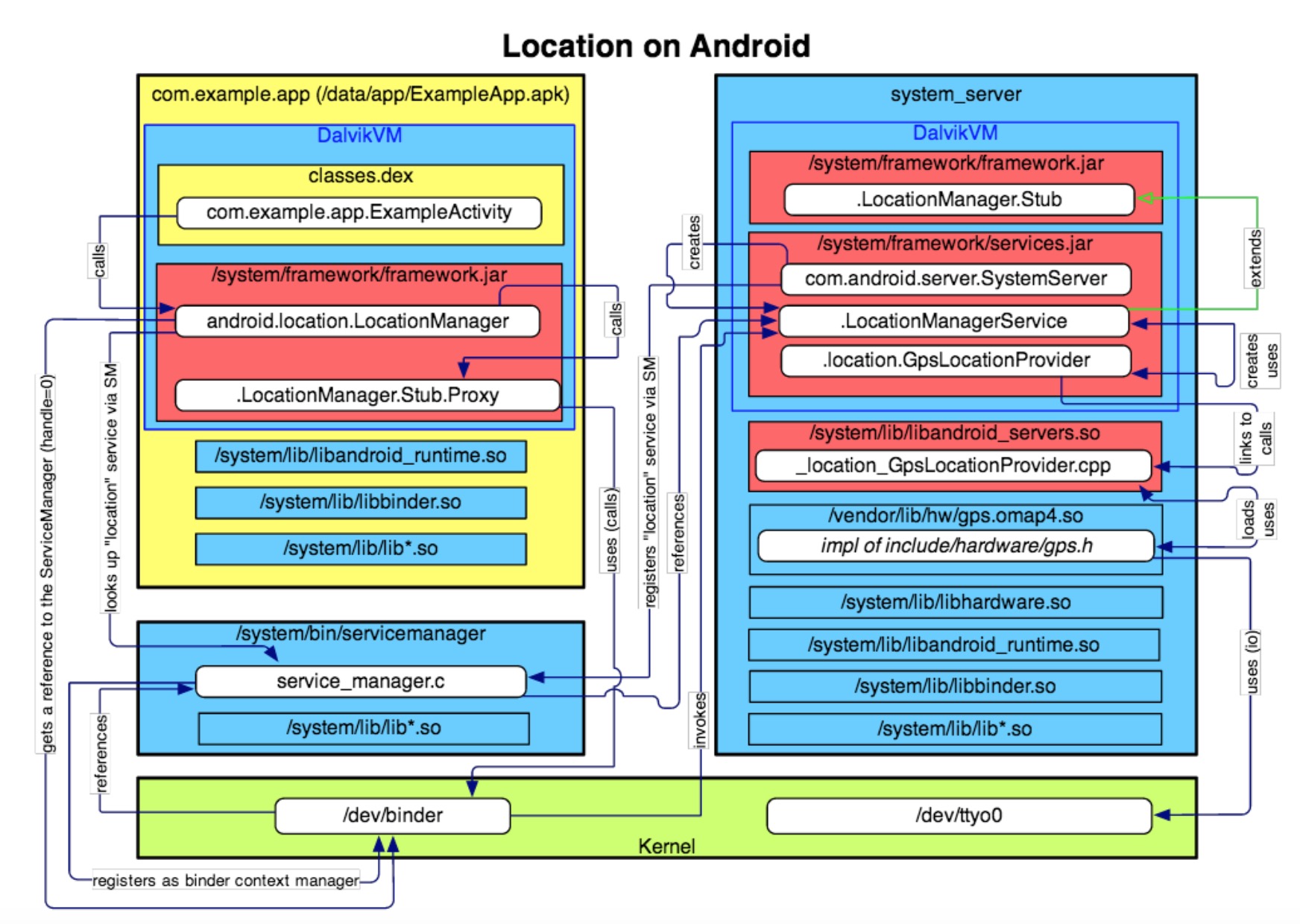
Location Service: An Example
AIDL
- AIDL是Android的语言,定义了基于Binder的服务接口
- AIDL遵循类似Java的接口语法,允许我们定义自己的“业务”方法
- 每一个基于Binder的服务都被定义在.aidl文件中,经典的命名如:IFooService.aidl,并且保存在src/目录下
src/com/example/app/IFooService.aidl
package com.example.app;
import com.example.app.Bar;
interface IFooService {
void save(inout Bar bar);
Bar getById(int id);
void delete(in Bar bar);
List<Bar> getAll();
}
- aidl的编译工具(Android SDK 部分)被用作从每个.aidl文件中提取真正的java接口(连同提供Android‘s android.os.IBinder的Stub)放到我们的/gen目录下
gen/com/example/app/IFooService.java
package com.example.app;
public interface IFooService extends android.os.IInterface {
public static abstract class Stub extends android.os.Binder implements com.example.app.IFooService {
...
public static com.example.app.IFooService asInterface(
android.os.IBinder obj) {
...
return new com.example.app.IFooService.Stub.Proxy(obj);
}
...
public boolean onTransact(int code, android.os.Parcel data, android.os.Parcel reply, int flags) throws android.os.RemoteException {
switch (code)
...
case TRANSACTION_save: {
...
com.example.app.Bar _arg0;
...
_arg0 = com.example.app.Bar.CREATOR.createFromParcel(data); this.save(_arg0);
...
}
...
}
...
}
...
private static class Proxy implements com.example.app.IFooService {
private android.os.IBinder mRemote;
...
public void save(com.example.app.Bar bar) throws android.os.RemoteException {
...
android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
...
bar.writeToParcel(_data, 0);
...
mRemote.transact(Stub.TRANSACTION_save, _data, _reply, 0);
...
}
}
}
void save(com.example.app.Bar bar) throws android.os.RemoteException;
com.example.app.Bar getById(int id) throws android.os.RemoteException;
void delete(com.example.app.Bar bar) throws android.os.RemoteException;
java.util.List<Bar> getAll() throws android.os.RemoteException;
}
注意:每次Eclipse ADT在src/目录下发现.aidl文件,它就会自动调用
-
AIDL支持以下的类型:
。null
。boolean,boolean[],byte,byte[],char[],int,int[],long,long[],float,float[],
double,double[]
。java.lang.CharSequence,java.lang.String (sent as UTF-20)
。java.io.FileDescriptor - transferred as a dup of the original file descriptor (points to the same underlying stream and position)
。java.io.Serializable - not efficient (too verbose)
。java.util.Map<String, Object> - of supported types (always reconstructed as
java.util.HashMap)
。android.os.Bundle - a specialized Map-wrapper that only accepts AIDL-supported data types
。java.util.List - of supported types (always reconstructed as java.util.ArrayList)
。java.lang.Object[] - of supported types (including primitive wrappers)
。android.util.SparseArray,android.util.SparseBooleanArray
。android.os.IBinder,android.os.IInterface - transferred by (globally unique) reference (as a "strong binder",a.k.a. handle) that can be used to call-back into the sender
。android.os.Parcelable - 自定义类型:
src/com/example/app/Bar.java
package com.example.app;
import android.os.Parcel;
import android.os.Parcelable;
public class Bar implements Parcelable {
private int id;
private String data;
public Bar(int id, String data) { this.id = id;
this.data = data;
}
// getters and setters omitted
...
public int describeContents() {
return 0;
}
public void writeToParcel(Parcel parcel, int flags) {
parcel.writeInt(this.id);
parcel.writeString(this.data);
}
public void readFromParcel(Parcel parcel) {
this.id = parcel.readInt();
this.data = parcel.readString();
}
public static final Parcelable.Creator<Bar> CREATOR = new Parcelable.Creator<Bar>() {
public Bar createFromParcel(Parcel parcel) {
return new Bar(parcel.readInt(), parcel.readString());
}
public Bar[] newArray(int size) {
return new Bar[size];
}
};

}
注意:public void readFromParcel(Parcel) 方法不是 Parcelable 接口定义的。这里是出于Bar的易变性考虑 -- 比如:我们期望远程的那端能够在 void save(inout Bar bar) 方法中修改它。
-
同理,public static final Parcelable.Creator
CREATOR 也不是 Parcelable 接口定义的(很明显)。它从 save 的事务中获取 _data ,从 getById 操作中获取 _reply ,重构了 Bar。 - 这些自定义的类必须在它们自己的.aidl文件中申明
src/com/example/app/Bar.aidl
package com.example.app;
parcelable Bar;
注意:AIDL接口必须导入parcelable自定义的类,即使它们在同一个包中。对于前面的示例,src/com/example/app/IFooService.aidl 必须导入com.example.app.Bar。
- AIDL定义的方法可以不传或传入多个参数,但是,必须返回一个值或者Void
-
所有的非基本类型的参数需要一个指定方向的标签,in、out、inout,这其中的一个
。基本数据类型的指向一直是in(可以省略)
。当编组数据的时候指向标签会传递给Binder,因此它会对性能有直接影响 -
所有的.aidl注释都应该被拷贝到生成的Java接口中(除了import和package语句前的)
- 只有以下的异常会默认支持:SecurityException, BadParcelableException, IllegalArgumentException, NullPointerException, IllegalStateException
- .aidl文件中,不支持静态成员
跨进程映射Binder对象引用
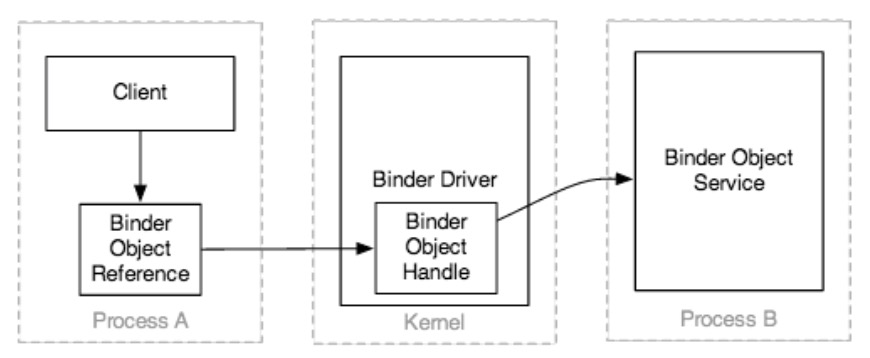
-
Binder对象的引用是以下的一种:
。在同一个进程中,Binder对象的一个真实的虚拟地址
。在另外一个进程中的,Binder对象的一个抽象的32位handle - 在每个的事务中,Binder驱动都会自动的将远程的binder handle映射成本地的地址,将本地的地址映射成远程的Binder handle
这种映射实现:
。Binder事务的目标
。IBinder对象的引用作为参数或返回值跨进程共享(嵌套在事务数据中)-
为了能够工作
。binder驱动在进程之间维持本地地址和远程handle(每一个进程都作为一个二进制树),因此,binder可以传送
。嵌套在事务中的引用是基于客户端提供的偏移 - Binder驱动不知道不与远程进程共享的Binder对象
。一旦一个新的Binder对象引用在事务中被发现,它就会记录在Binder驱动中
。任何时候,Binder引用与其它的进程共享,Binder驱动的引用计数器就会增长
。当进程消亡的时候,Binder驱动的计数器就会明确的减少或自动地减少
。当一个引用不再需要的时候,它的所有者就会提醒它可以释放掉,并且Binder会删除自己的映射
构建基于Binder的服务端和客户端
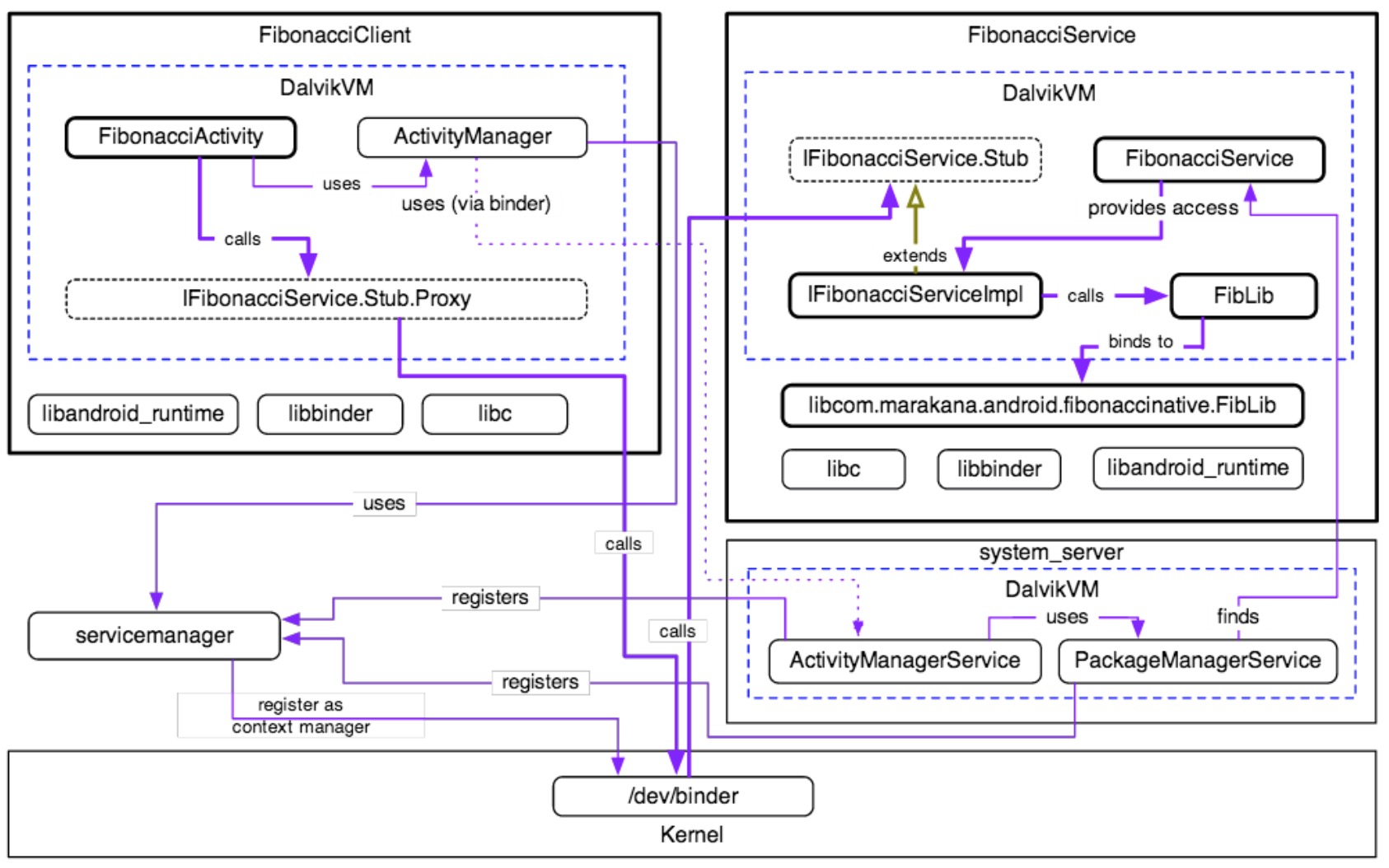
-
为了演示基于Binder的服务端和客户端(基于Fibonacci),我们将会创建三个独立的工程:
1.FibonacciCommon库工程 - 定义AIDL接口,自定义类型作为参数和返回值
2.FibonacciService工程 - 我们实现AIDL接口,并把它暴露给客户端
3.FibonacciClient工程 - 用它连接我们的AIDL服务 -
以下的代码是可用的
。一个ZIP归档文件 :https://github.com/marakana/FibonacciBinderDemo/zipball/master
。通过Git:git clone https://github.com/marakana/FibonacciBinderDemo.git - UI显示大概如下:
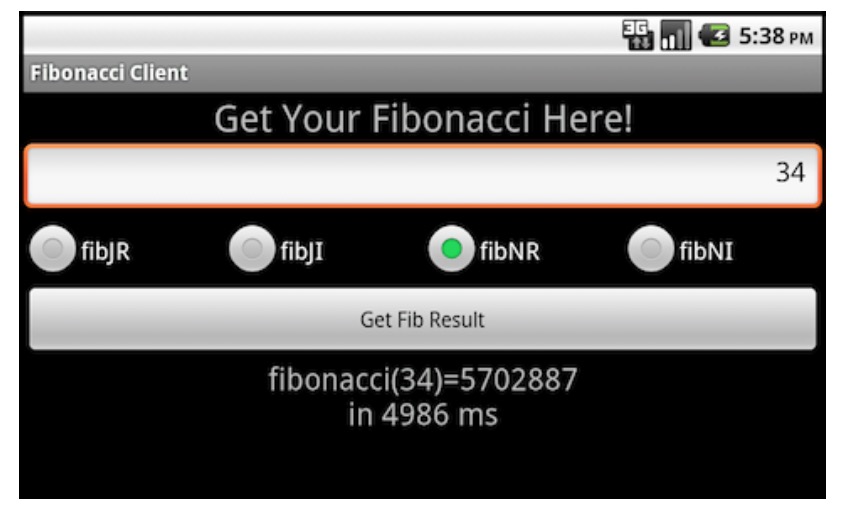
FibonacciCommon - Define AIDL Interface and Custom Types
FibonacciCommon - 定义AIDL接口和自定义类型
-
我们开始创建一个新的Android(库)工程,这是服务端和客户端可以共享的API文件(作为参数和返回值的一个AIDL接口和自定义类型)
。工程名:FibonacciCommon
。构建目标:Android 2.2+(API 8+)
。包名:com.marakana.android.fibonaccicommon
。最低SDK版本:8+
。不需要指定应用名或activity - 要转换成库工程,我们需要访问properties → Android → Library,然后,选中Library
- 我们也可以手动地添加 android.library=true 到 FibonacciCommon/default.properties 中,然后刷新该工程
- 因为库工程从来不会进入到实际的应用(APKS),所以我们可以简化清单文件:
FibonacciCommon/AndroidManifest.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.marakana.android.fibonaccicommon" android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0">
</manifest>
-
并且我们可以移除 FibonacciCommon/res/ 目录(例如:rm -fr FibonacciCommon/res/* )下的任何文件
- 我们现在已经准备好创建AIDL接口了
FibonacciCommon/src/com/marakana/android/fibonaccicommon/IFibonacciService.aidl
package com.marakana.android.fibonaccicommon;
import com.marakana.android.fibonaccicommon.FibonacciRequest;
import com.marakana.android.fibonaccicommon.FibonacciResponse;
interface IFibonacciService {
long fibJR(in long n);
long fibJI(in long n);
long fibNR(in long n);
long fibNI(in long n);
FibonacciResponse fib(in FibonacciRequest request);
}
- 很明显,我们的接口依赖两个自定义的Java类型,但是定义在它们自己的.aidl文件中
FibonacciCommon/src/com/marakana/android/fibonaccicommon/FibonacciRequest.java
package com.marakana.android.fibonaccicommon;
import android.os.Parcel; import android.os.Parcelable;
public class FibonacciRequest implements Parcelable {
public static enum Type {
RECURSIVE_JAVA, ITERATIVE_JAVA, RECURSIVE_NATIVE, ITERATIVE_NATIVE
}
private final long n;
private final Type type;
public FibonacciRequest(long n, Type type) {
this.n = n;
if (type == null){
throw new NullPointerException("Type must not be null");
}
this.type = type;
}
public long getN() {
return n;
}
public Type getType() {
return type;
}
public int describeContents() {
return 0;
}
public void writeToParcel(Parcel parcel, int flags) {
parcel.writeLong(this.n);
parcel.writeInt(this.type.ordinal());
}
public static final Parcelable.Creator<FibonacciRequest> CREATOR = new Parcelable.Creator<FibonacciRequest>() {
public FibonacciRequest createFromParcel(Parcel in) {
long n = in.readLong();
Type type = Type.values()[in.readInt()];
return new FibonacciRequest(n, type);
}
public FibonacciRequest[] newArray(int size) {
return new FibonacciRequest[size];
}
};
}
FibonacciCommon/src/com/marakana/android/fibonaccicommon/FibonacciRequest.aidl
package com.marakana.android.fibonaccicommon;
parcelable FibonacciRequest;
FibonacciCommon/src/com/marakana/android/fibonaccicommon/FibonacciResponse.java
package com.marakana.android.fibonaccicommon;
import android.os.Parcel; import android.os.Parcelable;
public class FibonacciResponse implements Parcelable {
private final long result;
private final long timeInMillis;
public FibonacciResponse(long result, long timeInMillis) {
this.result = result;
this.timeInMillis = timeInMillis;
}
public long getResult() {
return result;
}
public long getTimeInMillis() {
return timeInMillis;
}
public int describeContents() {
return 0;
}
public void writeToParcel(Parcel parcel, int flags) {
parcel.writeLong(this.result); parcel.writeLong(this.timeInMillis);
}
public static final Parcelable.Creator<FibonacciResponse> CREATOR = new Parcelable.Creator<FibonacciResponse>() {
public FibonacciResponse createFromParcel(Parcel in) {
return new FibonacciResponse(in.readLong(), in.readLong());
}
public FibonacciResponse[] newArray(int size) {
return new FibonacciResponse[size];
}
};
}
FibonacciCommon/src/com/marakana/android/fibonaccicommon/FibonacciResponse.aidl
package com.marakana.android.fibonaccicommon;
parcelable FibonacciResponse;
- 最后,我们可以准备查看自动生成的Java接口
FibonacciCommon/gen/com/marakana/android/fibonaccicommon/IFibonacciService.java
package com.marakana.android.fibonaccicommon;
public interface IFibonacciService extends android.os.IInterface {
public static abstract class Stub extends android.os.Binder
implements com.marakana.android.fibonacci.IFibonacciService {
...
public static com.marakana.android.fibonacci.IFibonacciService asInterface(android.os.IBinder obj) {
...
}
public android.os.IBinder asBinder() {
return this;
}
...
}
public long fibJR(long n) throws android.os.RemoteException;
public long fibJI(long n) throws android.os.RemoteException;
public long fibNR(long n) throws android.os.RemoteException;
public long fibNI(long n) throws android.os.RemoteException;
public com.marakana.android.fibonaccicommon.FibonacciResponse fib(
com.marakana.android.fibonaccicommon.FibonacciRequest request) throws android.os.RemoteException;
}
FibonacciService - 实现AIDL接口,并暴露给我们的客户端
-
我们开始创建一个新的Android工程,工程中有AIDL服务的实现和访问服务实现的机制(例如:绑定)
。工程名:FibonacciService
。编译目标:Android 2.2+(API 8+)
。包名:com.marakana.android.fibonacciservice
。应用名称:Fibonacci Service
。最小SDK: 8+
。不需要指定一个Activity - 为了能够访问common APIS,我们需要将工程跟FibonacciCommon链接:
-
工程名称 → Android → Library → Add... → FibonacciCommon
。最终, FibonacciService/default.properties 有了 android.library.reference.1=../FibonacciCommon ,并且 FibonacciService/.project 也链接到了 FibonacciCommon
-
我们的服务端将会使用实现了斐波那契算法的 com.marakana.android.fibonaccinative.FibLib
-
我们将FibonacciNative工程从Java类(和jni/implementation)中拷贝出(或移出)
。不要忘记在FibonacciService/下运行ndk-build去生成需要的本地库
-
我们现在已经准备好实现AIDL接口,通过扩展自动生成的com.marakana.android.fibonaccicommon.IFibonacciService.Stub(继承于android.os.Binder)
- FibonacciService/src/com/marakana/android/fibonacciservice/IFibonacciServiceImpl.java*
package com.marakana.android.fibonacciservice;
import android.os.SystemClock;
import android.util.Log;
import com.marakana.android.fibonaccicommon.FibonacciRequest;
import com.marakana.android.fibonaccicommon.FibonacciResponse;
import com.marakana.android.fibonaccicommon.IFibonacciService;
import com.marakana.android.fibonaccinative.FibLib;
public class IFibonacciServiceImpl extends IFibonacciService.Stub {
private static final String TAG = "IFibonacciServiceImpl";
public long fibJI(long n) {
Log.d(TAG, String.format("fibJI(%d)", n)); return FibLib.fibJI(n);
}
public long fibJR(long n) {
Log.d(TAG, String.format("fibJR(%d)", n)); return FibLib.fibJR(n);
}
public long fibNI(long n) {
Log.d(TAG, String.format("fibNI(%d)", n)); return FibLib.fibNI(n);
}
public long fibNR(long n) {
Log.d(TAG, String.format("fibNR(%d)", n)); return FibLib.fibNR(n);
}
public FibonacciResponse fib(FibonacciRequest request) {
Log.d(TAG,String.format("fib(%d, %s)", request.getN(), request.getType()));
long timeInMillis = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
long result;
switch (request.getType()) {
case ITERATIVE_JAVA:
result = this.fibJI(request.getN()); break;
case RECURSIVE_JAVA:
result = this.fibJR(request.getN()); break;
case ITERATIVE_NATIVE:
result = this.fibNI(request.getN()); break;
case RECURSIVE_NATIVE:
result = this.fibNR(request.getN()); break;
default: return null;
}
timeInMillis = SystemClock.uptimeMillis() - timeInMillis;
return new FibonacciResponse(result, timeInMillis);
}
}
暴露我们定义的AIDL服务实现给客户端
- 为了让客户端(调用者)使用我们的服务,首先它们需要绑定服务
- 但是,为了让它们绑定服务,首先我们需要暴露服务,通过android.app.Service's
onBind(Intent)实现
FibonacciService/src/com/marakana/android/fibonacciservice/FibonacciService.java
package com.marakana.android.fibonacciservice;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.util.Log;
public class FibonacciService extends Service { //1
private static final String TAG = "FibonacciService";
private IFibonacciServiceImpl service; //2
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
this.service = new IFibonacciServiceImpl(); //3
Log.d(TAG, "onCreate()'ed"); //5
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
Log.d(TAG, "onBind()'ed"); //5
return this.service; //4
}
@Override
public boolean onUnbind(Intent intent) {
Log.d(TAG, "onUnbind()'ed"); //5
return super.onUnbind(intent);
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
Log.d(TAG, "onDestroy()'ed");
this.service = null; super.onDestroy();
}
}
1、我们通过继承android.app.Service创建另外一个“service”。FibonacciService 对象的目的是提供访问我们的基于Binder的IFibonacciServiceImpl 对象
2、我们在这里简单的申明了一个本地的IFibonacciServiceImpl 引用,该引用是一个单例(例如:所有的客户端将会共享一个实例)。因为,我们的IFibonacciServiceImpl 不需要初始化的位置,所以我们可以在这里初始化,但是,我们选择推迟到onCreate() 方法中
3、现在,我们初始化了提供给客户端(在onBind(Intent)方法中)的IFibonacciServiceImpl 。如果,我们的IFibonacciServiceImpl 需要访问Context,我们可以传递一个引用给它(例如:android.app.Service ,实现了android.content.Context )。很多基于Binder的服务端使用context去访问其它平台的方法
4、我们在这里提供客户端访问IFibonacciServiceImpl 对象的接口。我们选择,只拥有一个IFibonacciServiceImpl 实例对象(因此所有的客户端都可以共享它),但是,我们也可以给每一个客户端提供一个IFibonacciServiceImpl 实例对象
5、我们添加一些日志,这样跟踪服务的生命周期就会简单
-
最后,我们在AndroidManifest.xml 中注册FibonacciService ,所以,客户端可以找到它
- FibonacciService/AndroidManifest.xml*
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.marakana.android.fibonacciservice" android:versionCode="1" android:versionName="1.0">
<uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="8" />
<application android:icon="@drawable/icon" android:label="@string/app_name">
<service android:name=".FibonacciService">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.marakana.android.fibonaccicommon.IFibonacciService" /> <!-- 1 -->
</intent-filter>
</service>
</application>
</manifest>
1、名称可以随便定义,但是,我们通常使用派生的AIDL接口的全名
FibonacciClient - 使用基于Binder的AIDL服务
-
我们开始创建一个新的Android工程,这个工程是我们之前实现的AIDL Service的客户端
。工程名:FibonacciClient
。构建的目标:Android 2.2+(API 8+)
。包名:com.marakana.android.fibonacciclient
。应用名:Fibonacci Client
。创建的Activity:FibonacciActivity* Activity中的大部分代码来自于 FibonacciNative。最小SDK版本:8+
- 我们需要将工程链接到FibonacciCommon上,以便能够访问公有的APIs:
-
project properties → Android → Library → Add... → FibonacciCommon
。结果,FibonacciClient/default.properties 中有android.library.reference.1=../FibonacciCommon 和FibonacciClient/.classpath ,并且FibonacciClient/.project 也链接到了FibonacciCommon
。作为一种替代,我们可以避免首先创建FibonacciCommon
。FibonacciService 和 FibonacciClient 都需要拷贝:IFibonacciService.aidl、 FibonacciRequest.aidl、 FibonacciResponse.aidl、 FibonacciResult.java、 FibonacciResponse.java++
。但是,我们不喜欢重复的代码(即使在运行时二进制文件会重复) -
我们的客户端将会使用 FibonacciNative 应用中的字符串和布局资源
- FibonacciClient/res/values/strings.xml*
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<string name="hello">Get Your Fibonacci Here!</string>
<string name="app_name">Fibonacci Client</string>
<string name="input_hint">Enter N</string>
<string name="input_error">Numbers only!</string>
<string name="button_text">Get Fib Result</string>
<string name="progress_text">Calculating...</string>
<string name="fib_error">Failed to get Fibonacci result</string>
<string name="type_fib_jr">fibJR</string>
<string name="type_fib_ji">fibJI</string>
<string name="type_fib_nr">fibNR</string>
<string name="type_fib_ni">fibNI</string>
</resources>
- FibonacciClient/res/layout/main.xml*
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent">
<TextView android:text="@string/hello" android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:textSize="25sp" android:gravity="center"/>
<EditText android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="match_parent" android:id="@+id/input" android:hint="@string/input_hint" android:inputType="number" android:gravity="right" />
<RadioGroup android:orientation="horizontal" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:id="@+id/type" android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<RadioButton android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:checked="true" android:id="@+id/type_fib_jr" android:text="@string/type_fib_jr"
android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_weight="1" />
<RadioButton android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/type_fib_ji" android:text="@string/type_fib_ji"
android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_weight="1" />
<RadioButton android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/type_fib_nr" android:text="@string/type_fib_nr"
android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_weight="1" />
<RadioButton android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/type_fib_ni" android:text="@string/type_fib_ni"
android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_weight="1" />
</RadioGroup>
<Button android:text="@string/button_text" android:id="@+id/button" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<TextView android:id="@+id/output" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:textSize="20sp"
android:gravity="center|top"/>
</LinearLayout>
- 我们现在准备实现客户端
FibonacciClient/src/com/marakana/android/fibonacciclient/FibonacciActivity.java
package com.marakana.android.fibonacciclient;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.ProgressDialog;
import android.content.ComponentName; import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection; import android.os.AsyncTask;

import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.RemoteException;
import android.os.SystemClock;
import android.text.TextUtils;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener; import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.RadioGroup;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.widget.Toast;
import com.marakana.android.fibonaccicommon.FibonacciRequest;
import com.marakana.android.fibonaccicommon.FibonacciResponse;
import com.marakana.android.fibonaccicommon.IFibonacciService;
public class FibonacciActivity extends Activity implements OnClickListener, ServiceConnection {
private static final String TAG = "FibonacciActivity";
private EditText input; // our input n
private Button button; // trigger for fibonacci calcualtion
private RadioGroup type; // fibonacci implementation type
private TextView output; // destination for fibonacci result
private IFibonacciService service; // reference to our service
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
super.setContentView(R.layout.main);
// connect to our UI elements
this.input = (EditText) super.findViewById(R.id.input);
this.button = (Button) super.findViewById(R.id.button);
this.type = (RadioGroup) super.findViewById(R.id.type);
this.output = (TextView) super.findViewById(R.id.output); // request button click call-backs via onClick(View) method
this.button.setOnClickListener(this);
// the button will be enabled once we connect to the service
this.button.setEnabled(false);
}
@Override
protected void onResume() {
Log.d(TAG, "onResume()'ed");
super.onResume();
// Bind to our FibonacciService service, by looking it up by its name
// and passing ourselves as the ServiceConnection object
// We'll get the actual IFibonacciService via a callback to
// onServiceConnected() below
if (!super.bindService(new Intent(IFibonacciService.class.getName()),
this, BIND_AUTO_CREATE)) {
Log.w(TAG, "Failed to bind to service");
}
}
 @Override
protected void onPause() {
Log.d(TAG, "onPause()'ed");
super.onPause();
// No need to keep the service bound (and alive) any longer than
// necessary
super.unbindService(this);
}
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
Log.d(TAG, "onServiceConnected()'ed to " + name);
// finally we can get to our IFibonacciService
this.service = IFibonacciService.Stub.asInterface(service);
// enable the button, because the IFibonacciService is initialized
this.button.setEnabled(true); }
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
Log.d(TAG, "onServiceDisconnected()'ed to " + name);
// our IFibonacciService service is no longer connected this.service = null;
// disabled the button, since we cannot use IFibonacciService
this.button.setEnabled(false); }
// handle button clicks
public void onClick(View view) {
// parse n from input (or report errors) final long n;
String s = this.input.getText().toString();
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(s)) {
return; }
try {
n = Long.parseLong(s);
} catch (NumberFormatException e){
this.input.setError(super.getText(R.string.input_error));
return;
}
// build the request object
final FibonacciRequest.Type type;
switch (FibonacciActivity.this.type.getCheckedRadioButtonId()) {
case R.id.type_fib_jr:
type = FibonacciRequest.Type.RECURSIVE_JAVA;
break;
case R.id.type_fib_ji:
type = FibonacciRequest.Type.ITERATIVE_JAVA;
break;
case R.id.type_fib_nr:
type = FibonacciRequest.Type.RECURSIVE_NATIVE;
break;
case R.id.type_fib_ni:
type = FibonacciRequest.Type.ITERATIVE_NATIVE;
break;
default:
return;
}
final FibonacciRequest request = new FibonacciRequest(n, type);
// showing the user that the calculation is in progress
final ProgressDialog dialog = ProgressDialog.show(this, "",
super.getText(R.string.progress_text), true);
// since the calculation can take a long time, we do it in a separate
// thread to avoid blocking the UI
new AsyncTask<Void, Void, String>() {
@Override
protected String doInBackground(Void... params) {
// this method runs in a background thread
try {
long totalTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
FibonacciResponse response = FibonacciActivity.this.service.fib(request);
totalTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis() - totalTime; // generate the result
return String.format(
"fibonacci(%d)=%d\nin %d ms\n(+ %d ms)", n, response.getResult(), response.getTimeInMillis(), totalTime - response.getTimeInMillis());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.wtf(TAG, "Failed to communicate with the service", e); return null;
}
}
@Override
protected void onPostExecute(String result) {
// get rid of the dialog
dialog.dismiss();
if (result == null) {
// handle error
Toast.makeText(FibonacciActivity.this, R.string.fib_error, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
} else {
// show the result to the user FibonacciActivity.this.output.setText(result);
}
}
}.execute(); // run our AsyncTask
}
}
注意:我们应该尽量避免在Activity中调用匿名的AsyncTask。这里我们走了一个捷径。
-
我们的Activity应该已经在 AndroidManifest.xml 文件中注册过
- FibonacciClient/AndroidManifest.xml*
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:versionCode="1" android:versionName="1.0" package="com.marakana.android.fibonacciclient">
<uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="8" />
<application android:icon="@drawable/icon" android:label="@string/app_name">
<activity android:name="com.marakana.android.fibonacciclient.FibonacciActivity" android:label="@string/app_name">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>
- 结果应该是这样的:
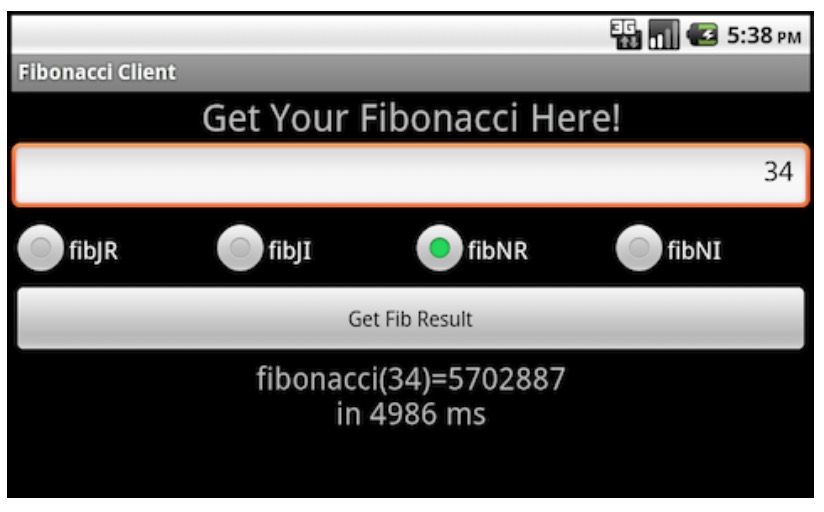
异步 Binder IPC
- 在 AIDL 接口中申明,Binder 允许客户端与服务端之间异步通信
- 当然,我们仍然关心结果,通常异步回调都是通过监听器回调的方式
- 客户端给提供了一个引用作为回调的监听器,然后,当监听器调用的时候,客户端和服务端的角色就会调换:客户端端的监听器变成了服务端的,服务端的监听器变成了客户端的
- 最好的解释是通过一个示例(基于 Fibonacci)
-
代码是可用的
。一个ZIP存档文件:https://github.com/marakana/FibonacciAsyncBinderDemo/zipball/master
。通过Git:git clone https://github.com/marakana/FibonacciAsyncBinderDemo.git
FibonacciCommon - 定义一个单向的 AIDL 服务
- 首先,我们需要一个监听器,它自己是单向的"服务":
FibonacciCommon/src/com/marakana/android/fibonaccicommon/IFibonacciServiceResponseListener.aidl:
package com.marakana.android.fibonaccicommon;
import com.marakana.android.fibonaccicommon.FibonacciRequest;
import com.marakana.android.fibonaccicommon.FibonacciResponse;
oneway interface IFibonacciServiceResponseListener {
void onResponse(in FibonacciResponse response);
}
- 现在我们可以创建我们自己的单向的(例如:异步的) 接口:
FibonacciCommon/src/com/marakana/android/fibonaccicommon/IFibonacciService.aidl:
package com.marakana.android.fibonaccicommon;
import com.marakana.android.fibonaccicommon.FibonacciRequest;
import com.marakana.android.fibonaccicommon.FibonacciResponse;
import com.marakana.android.fibonaccicommon.IFibonacciServiceResponseListener;
oneway interface IFibonacciService {
void fib(in FibonacciRequest request, in IFibonacciServiceResponseListener listener);
}
FibonacciService - 实现异步的 AIDL 服务
- 服务的实现调用这个监听器,而不是返回一个结果:
FibonacciService/src/com/marakana/android/fibonacciservice/IFibonacciServiceImpl.java:
package com.marakana.android.fibonacciservice;
import android.os.RemoteException;
import android.os.SystemClock; import android.util.Log;
import com.marakana.android.fibonaccicommon.FibonacciRequest;
import com.marakana.android.fibonaccicommon.FibonacciResponse;
import com.marakana.android.fibonaccicommon.IFibonacciService;
import com.marakana.android.fibonaccicommon.IFibonacciServiceResponseListener;
import com.marakana.android.fibonaccinative.FibLib;
public class IFibonacciServiceImpl extends IFibonacciService.Stub {
private static final String TAG = "IFibonacciServiceImpl";
@Override
public void fib(FibonacciRequest request,
IFibonacciServiceResponseListener listener) throws RemoteException {
long n = request.getN();
Log.d(TAG, "fib(" + n + ")");
long timeInMillis = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
long result;
switch (request.getType()) {
case ITERATIVE_JAVA:
result = FibLib.fibJI(n);
break;
case RECURSIVE_JAVA:
result = FibLib.fibJR(n);
break;
case ITERATIVE_NATIVE:
result = FibLib.fibNI(n);
break;
case RECURSIVE_NATIVE:
result = FibLib.fibNR(n);
break;
default:
result = 0;
}
timeInMillis = SystemClock.uptimeMillis() - timeInMillis;
Log.d(TAG, String.format("Got fib(%d) = %d in %d ms", n, result,timeInMillis));
listener.onResponse(new FibonacciResponse(result, timeInMillis));
}
}
注意:服务不会因监听返回而阻塞,因为,监听器本身也是单向的
FibonacciClient - 实现异步的 AIDL 客户端
- 最后,实现的客户端,它本身也必然实现服务端的监听器
FibonacciClient/src/com/marakana/android/fibonacciclient/FibonacciActivity.java:
package com.marakana.android.fibonacciclient;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.Dialog;
import android.app.ProgressDialog;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.Message;
import android.os.RemoteException;
import android.os.SystemClock;
import android.text.TextUtils;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.RadioGroup;
import android.widget.TextView;
import com.marakana.android.fibonaccicommon.FibonacciRequest;
import com.marakana.android.fibonaccicommon.FibonacciResponse;
import com.marakana.android.fibonaccicommon.IFibonacciService;
import com.marakana.android.fibonaccicommon.IFibonacciServiceResponseListener;
public class FibonacciActivity extends Activity implements OnClickListener, ServiceConnection {
private static final String TAG = "FibonacciActivity";
// the id of a message to our response handler
private static final int RESPONSE_MESSAGE_ID = 1;
// the id of a progress dialog that we'll be creating
private static final int PROGRESS_DIALOG_ID = 1;
private EditText input; // our input n
private Button button; // trigger for fibonacci calcualtion
private RadioGroup type; // fibonacci implementation type
private TextView output; // destination for fibonacci result
private IFibonacciService service; // reference to our service
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
super.setContentView(R.layout.main);
// connect to our UI elements
this.input = (EditText) super.findViewById(R.id.input);
this.button = (Button) super.findViewById(R.id.button);
this.type = (RadioGroup) super.findViewById(R.id.type);
this.output = (TextView) super.findViewById(R.id.output); // request button click call-backs via onClick(View) method
this.button.setOnClickListener(this);
// the button will be enabled once we connect to the service
this.button.setEnabled(false);
}
@Override
protected void onResume() {
Log.d(TAG, "onResume()'ed");
super.onResume();
// Bind to our FibonacciService service, by looking it up by its name
// and passing ourselves as the ServiceConnection object
// We'll get the actual IFibonacciService via a callback to
// onServiceConnected() below
if (!super.bindService(new Intent(IFibonacciService.class.getName()),this, BIND_AUTO_CREATE)) {
Log.w(TAG, "Failed to bind to service");
}
}
@Override
protected void onPause() {
Log.d(TAG, "onPause()'ed");
super.onPause();
// No need to keep the service bound (and alive) any longer than
// necessary
super.unbindService(this);
}
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
Log.d(TAG, "onServiceConnected()'ed to " + name);
// finally we can get to our IFibonacciService
this.service = IFibonacciService.Stub.asInterface(service);
// enable the button, because the IFibonacciService is initialized
this.button.setEnabled(true);
}
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
Log.d(TAG, "onServiceDisconnected()'ed to " + name);
// our IFibonacciService service is no longer connected
this.service = null;
// disabled the button, since we cannot use IFibonacciService
this.button.setEnabled(false);
}
// handle button clicks
public void onClick(View view) {
// parse n from input (or report errors)
final long n;
String s = this.input.getText().toString();
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(s)) {
return;
}
try {
n = Long.parseLong(s);
} catch (NumberFormatException e)
{
this.input.setError(super.getText(R.string.input_error));
return;
}
// build the request object
final FibonacciRequest.Type type;
switch (FibonacciActivity.this.type.getCheckedRadioButtonId()) {
case R.id.type_fib_jr:
type = FibonacciRequest.Type.RECURSIVE_JAVA;
break;
case R.id.type_fib_ji:
type = FibonacciRequest.Type.ITERATIVE_JAVA;
break;
case R.id.type_fib_nr:
type = FibonacciRequest.Type.RECURSIVE_NATIVE;
break;
case R.id.type_fib_ni:
type = FibonacciRequest.Type.ITERATIVE_NATIVE;
break;
default:
return;
}
final FibonacciRequest request = new FibonacciRequest(n, type);
try {
Log.d(TAG, "Submitting request...");
long time = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
// submit the request; the response will come to responseListener this.service.fib(request, this.responseListener);
time = SystemClock.uptimeMillis() - time;
Log.d(TAG, "Submited request in " + time + " ms");
// this dialog will be dismissed/removed by responseHandler super.showDialog(PROGRESS_DIALOG_ID);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.wtf(TAG, "Failed to communicate with the service", e);
}
}
}
注意:我们的监听器不应该持有 Activity 的强引用(但是它确实是,因为它是匿名的内部类),但是,在当前情况下,为了简明起见,我们忽略了它的正确性
通过Binder共享内存
-
Binder事务处理的数据是通信中的部分拷贝——如果传送很多数据是不明智的
。事实上,binder通过事务强制限制了发送数据的大小
-
如果我们想共享文件中的数据,我们只需要发送文件的描述符
。这是我们要求媒体播放器去播放音频、视频文件的方式——我们只是发送文件的描述符到软件驱动中
-
如果我们想要发送的数据在内存中,我们可以分多次发送,而不是试图一次发送所有的数据
。让我们的设计复杂化
-
可选,我们可以利用Android's ashmem(Ashmem匿名共享内存)工具
。它的Java封装器android.os.MemoryFile 不是用于第三方app共享内存
。丢到本地(通过JNI),然后是直接使用ashmem -
本地共享内存通过 frameworks/base/libs/binder/Parcel.cpp 来实现:
。void Parcel::writeBlob(size_t len, WritableBlob outBlob)
。status_t Parcel::readBlob(size_t len, ReadableBlob outBlob) -
以下是简略的实现:
- Client
```C++
size_t len = 4096;
int fd = ashmem_create_region("Parcel Blob", len);
ashmem_set_prot_region(fd, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE);
void* ptr = mmap(NULL, len, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, fd, 0);
ashmem_set_prot_region(fd, PROT_READ);
writeFileDescriptor(fd, true);
// write into ptr for len as desired
...
munmap(ptr, len);
close(fd);
* Service
```C
int fd = readFileDescriptor();
void* ptr = mmap(NULL, len, PROT_READ, MAP_SHARED, fd, 0); // read from ptr up to len as desired
...
munmap(ptr, len);
注意:为了方便删除错误处理。并且,writeFileDescriptor(...) readFileDescriptor(...) 是libbinder提供的
Binder的局限性
- 每个进程最多支持15个Binder线程
frameworks/base/libs/binder/ProcessState.cpp
...
static int open_driver() {
int fd = open("/dev/binder", O_RDWR); if (fd >= 0) {
...
size_t maxThreads = 15;
result = ioctl(fd, BINDER_SET_MAX_THREADS, &maxThreads); ...
} else {
...
}
return fd;
}
...
。避免阻塞Binder线程
。如果我们需要执行一个长连接的任务,最好创建我们自己的线程-
Binder限制运行在每个进程中的并发事务的缓存为1M
。如果参数或返回值的大小超过了缓存,就会抛出TransactionTooLargeException
。因为指定进程中的所有事务的缓存都是共享的,所以很多中等大小的事务也会耗尽缓存
。当TransactionTooLargeException 异常抛出的时候,我们不知道是发送请求出了错,还是接收响应出了错
。让事务数据尽量小,或者使用共享内存(ashmem)
Binder - 安全机制
-
Binder确实需要直接处理“安全”问题,但是,它只会在“可信的”执行环境和DAC中运行
- Binder驱动只允许注册一个 CONTEXT_MGR(例如:servicemanager )
drivers/staging/android/binder.c:
...
static long binder_ioctl(struct file * filp, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg) {
...
switch (cmd) {
...
case BINDER_SET_CONTEXT_MGR:
if (binder_context_mgr_node != NULL) {
printk(KERN_ERR "binder: BINDER_SET_CONTEXT_MGR already set\n");
ret = -EBUSY;
goto err;
}
...
binder_context_mgr_node = binder_new_node(proc, NULL, NULL); ...
}
...
...
- servicemanager同样也只允许从信任的UID中注册(比如:system、radio、media 等等)
frameworks/base/cmds/servicemanager/service_manager.c:
...
static struct {
unsigned uid;
const char * name;
} allowed[] = {
#ifdef LVMX
{ AID_MEDIA,"com.lifevibes.mx.ipc" },
#endif
{ AID_MEDIA, "media.audio_flinger" },
{ AID_MEDIA, "media.player" },
{ AID_MEDIA, "media.camera" },
{ AID_MEDIA, "media.audio_policy" },
{ AID_DRM, "drm.drmManager" },
{ AID_NFC, "nfc" },
{ AID_RADIO, "radio.phone" },
{ AID_RADIO, "radio.sms" },
{ AID_RADIO, "radio.phonesubinfo" },
{ AID_RADIO, "radio.simphonebook" },
/* TODO: remove after phone services are updated: */
{ AID_RADIO, "phone" },
{ AID_RADIO, "sip" },
{ AID_RADIO, "isms" },
{ AID_RADIO, "iphonesubinfo" },
{ AID_RADIO, "simphonebook" },
};
...
int svc_can_register(unsigned uid, uint16_t * name)
{
unsigned n;
if ((uid == 0) || (uid == AID_SYSTEM))
return 1;
for (n = 0; n < sizeof(allowed) / sizeof(allowed[0]); n++)
if ((uid == allowed[n].uid) && str16eq(name, allowed[n].name))
return 1;
return 0;
}
...
int do_add_service(struct binder_state * bs,
uint16_t * s, unsigned len, void * ptr, unsigned uid)
{
...
if (!svc_can_register(uid, s)) {
LOGE("add_service('%s',%p) uid=%d - PERMISSION DENIED\n",
str8(s), ptr, uid); return -1;
}
...
}
...
-
每个Binder事务发送者的UID和PID很容易被访问到:
。android.os.Binder.getCallingPid()
。android.os.Binder.getCallingUid() -
一旦我们知道如何访问UID,我们就可以很容易的解决调用app的问题,通过PackageManager.getPackagesForUid(int uid)
-
一旦我们知道如何调用app,我们就可以很容易的检查app是否有权限,通过PackageManager.getPackageInfo(String packageName, int flags) (检查PackageManager.GET_PERMISSIONS 标记)
-
但是,更简单的方式是:
。Context.checkCallingOrSelfPermission(String permission),如果调用的进程授予了权限就会返回PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED,否则返回PackageManager.PERMISSION_DENIED
。Context.enforceCallingPermission(String permission, String message)——如果调用者没有请求的权限就会抛出SecurityException异常
- 以下显示应用框架服务是如何执行权限的
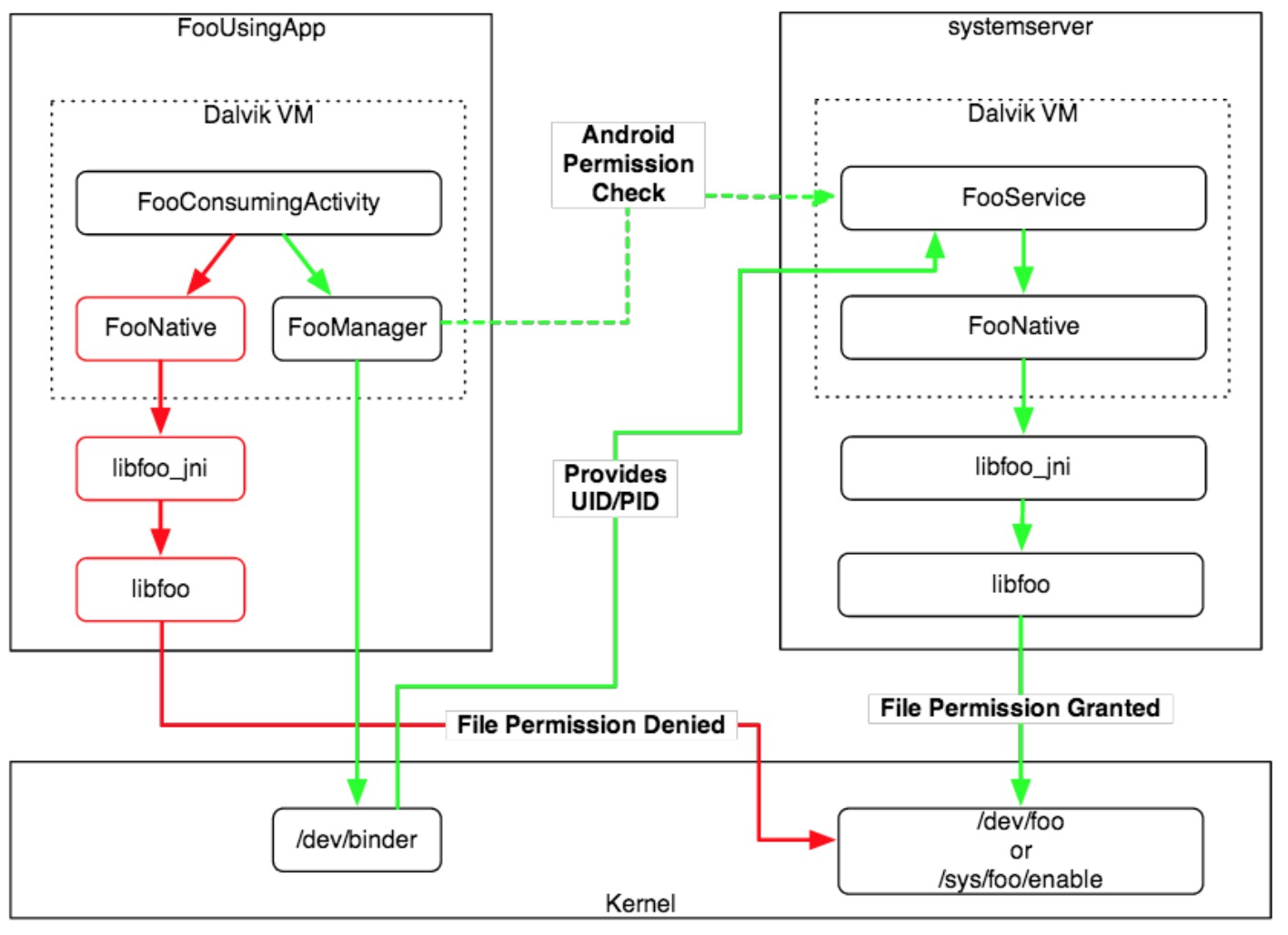
For example:
frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/VibratorService.java:
package com.android.server;
...
public class VibratorService extends IVibratorService.Stub {
...
public void vibrate(long milliseconds, IBinder token) {
if (mContext.checkCallingOrSelfPermission(android.Manifest.permission.VIBRATE) != PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED) {
throw new SecurityException("Requires VIBRATE permission");
}
...
}
...
}
frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/LocationManagerService.java:
package com.android.server;
...
public class LocationManagerService extends ILocationManager.Stub implements Runnable {
...
private static final String ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION =
android.Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION;
private static final String ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION =
android.Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION;
...
private void checkPermissionsSafe(String provider) {
if ((LocationManager.GPS_PROVIDER.equals(provider)
|| LocationManager.PASSIVE_PROVIDER.equals(provider))
&& (mContext.checkCallingOrSelfPermission(ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION)
!= PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED)) {
throw new SecurityException("Provider " + provider
+ " requires ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION permission");
}
if (LocationManager.NETWORK_PROVIDER.equals(provider)
&& (mContext.checkCallingOrSelfPermission(ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION) != PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED)
&& (mContext.checkCallingOrSelfPermission(ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION) != PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED)) {
throw new SecurityException("Provider " + provider
+ " requires ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION or ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION permission");
}
}
...
private Location _getLastKnownLocationLocked(String provider) {
checkPermissionsSafe(provider);
...
}
...
public Location getLastKnownLocation(String provider) {
...
_getLastKnownLocationLocked(provider);
...
}
}
Binder消亡通知
- 持有IBinder对象的引用,我们可以:
- 询问远程对象是否存活,通过 Binder.isBinderAlive()and Binder.pingBinder()
- 获取到远程对象消亡的通知,通过 Binder.linkToDeath(IBinder.DeathRecipient recipient, int flags)
- 如果我们想要清除与远程Binder对象关联的不可用资源(如:监听器)
For example:
frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/LocationManagerService.java:
public class LocationManagerService extends ILocationManager.Stub implements Runnable
{
...
private Receiver getReceiver(ILocationListener listener) {
IBinder binder = listener.asBinder();
Receiver receiver = mReceivers.get(binder);
if (receiver == null) {
receiver = new Receiver(listener);
...
receiver.getListener().asBinder().linkToDeath(receiver, 0);
...
}
return receiver;
}
private final class Receiver implements IBinder.DeathRecipient,
PendingIntent.OnFinished {
final ILocationListener mListener;
...
Receiver(ILocationListener listener) {
mListener = listener;
...
}
...
public void binderDied() {
...
removeUpdatesLocked(this);
}
...
}
...
}
Binder报告
-
在 active/failed 事务中,Binder驱动通过 /proc/binder/ 报告多种状态
。/proc/binder/failed_transaction_log
。/proc/binder/state
。/proc/binder/stats
。/proc/binder/transaction_log
。/proc/binder/transactions
。/proc/binder/proc/
注意:在设备中将 /sys/kernel/debug/binder 替换成 /proc/binder 的时候,设置 debugfs 为 enable
Additional Binder Resources
Android Binder by Thorsten Schreiber from Ruhr-Universität Bochum
Android Binder IPC Mechanism - 0xLab by Jim Huang (黄敬群) from 0xlab
Android’s Binder by Ken from Ken’s Space
Dianne Hackborn on Binder in Android on Linux Kernel Mailing List archive (LKML.ORG)
Android Binder on elinux.org
Share memory using ashmem and binder in the android framework
Introduction to OpenBinder and Interview with Dianne Hackborn
Open Binder Documentation
Binder IPC - A walk-though native IAudioFlinger::setMode call
Summary
We learned about:
Why Android needs IPC
What is Binder and how it differs from other forms of IPC
Binder vs Intent/ContentProvider/Messenger-based IPC
Binder Terminology
Binder Communication and Discovery Model
AIDL
Binder Object Reference Mapping
Synchronous vs Async Binder Invocations
Memory Sharing
Binder Limitations
Security Implications
Death Notification
Reporting
Questions?
Didn’t we run out of time by now? :-)
Thank you for your patience!
Slides and screencast from this class will be posted to: http://mrkn.co/bgnhg You can follow me here:
@agargenta
+Aleksandar Gargenta http://marakana.com/s/author/1/aleksandar_gargenta
This slide-deck is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.