为什么在Android使用ClassLoader.getResourceAsStream会如此影响性能
通过对 NimbleDroid 进行各种各样的分析,我们找到一些可能会让 Android 应用性能,应用启动速度和响应时间受到较大负面影响的陷阱。而 ClassLoader.getResourceAsStream() 就是其中之一,该方法允许应用访问给定名称的对应资源。在 Java 开发中,这个方法很常用,但它在 Android 开发中真的不推荐使用,因为该方法会在应用首次调用它时对性能造成很大的负面影响。我们分析了大量的 App 和 SDK,结果显示:超过 10% 的 App 和 20% 的 SDK 都因为这个方法性能显著下降。这里面到底发生了什么呢?想知道的话就向下读吧!
具体例子
Amazon 的 Kindle App Android 端,作为拥有数百万下载数的超级应用,却因为这个方法的使用造成了 1315ms 的延迟。(分析版本是 Kindle 4.15.0.48)
TuneIn 13.6.1 则是 1447ms 的延迟,在 TuneIn 中,应用调用了该方法两次,但第二次调用的速度显然快多了(6ms)。
下面是因为该方法性能受到影响的应用:
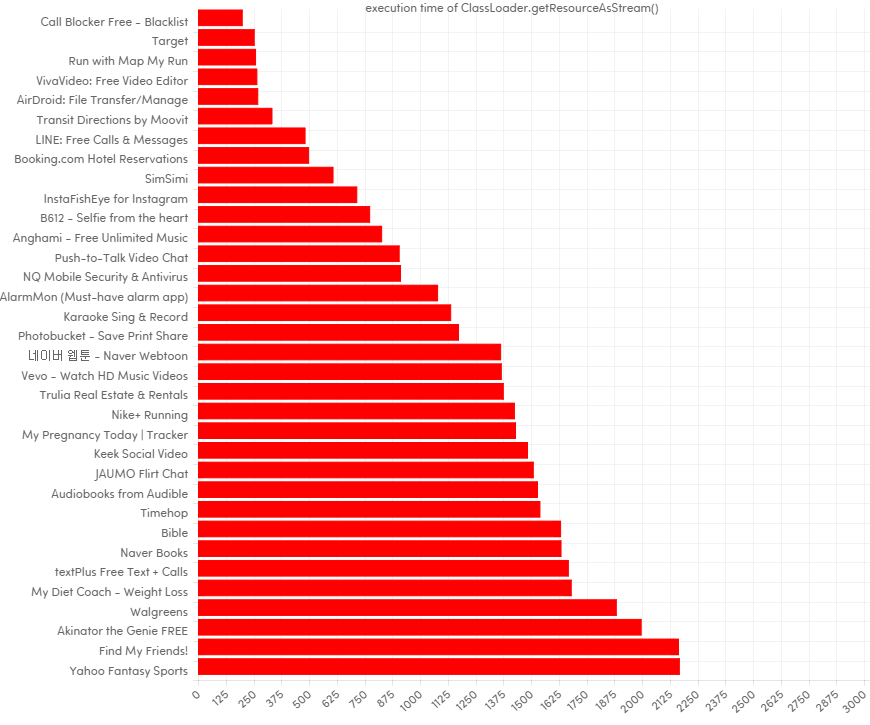
重要的事情说三遍:
在我们分析的应用中,超过 10% 的应用都遇到了这个问题。
在我们分析的应用中,超过 10% 的应用都遇到了这个问题。
在我们分析的应用中,超过 10% 的应用都遇到了这个问题。
调用 getResourceAsStream 方法的 SDK
为简短起见,我们用与某些确切的 Service 关联的库(例如 Amazon 的 AWS)和那些没有的库(例如 Joda-Time)的 SDK 去参考该方法对性能的影响。
通常情况下,开发者不会直接调用 getResourceAsStream 方法,相反,该方法是由开发者使用的部分 SDK 调用的。由于开发者一般不会在意 SDK 的内部实现,因此他们也很难注意到他们开发的应用会存在这样的问题。
下面我列出部分调用了 getResourceAsStream 方法的常用 SDK:
- mobileCore
- SLF4J
- StartApp
- Joda-Time
- TapJoy
- Google Dependency Injection
- BugSense
- RoboGuice
- OrmLite
- Appnext
- Apache log4j
- Twitter4J
- Appcelerator Titanium
- LibPhoneNumbers (Google)
- Amazon AWS
总的来说,在我们分析的 SDK 中,超过 20% 的 SDK 都存在这个问题 - 上面这张列表只列出其中一小部分 SDK,因为全列出来的话文章会变得很长很长很长……那为什么 getResourceAsStream 方法会在这么多 SDK 中被调用?它有什么特别的优势么?答案是:getResourceAsStream 方法在 Android 以外的平台使用时性能表现都很不错,然而在 Android 中并不是这样。因此,由于许多 Android 程序员都是 Java 程序员转行的,而且这些人在开发时更倾向使用一些以前用过的库,因此他们开发出来的 Android 应用/库就受到此问题的影响了。
为什么 getResourceAsStream 在 Android 中性能表现如此糟糕?
那么很多人可能会问了,为什么这个方法到了 Android 就显得如此水土不服?我们团队在进行深入调查后发现,当它在 Android 中第一次被调用,Android 执行了三个非常慢的操作:
- 将 APK 文件作为 zip 文件打开,并索引所有 zip 表项
- 再一次执行 1 的操作
- 验证 APK 签名是否符合规范
不得不说,这些操作都是非常非常非常耗时的,而且需要的时间与应用的大小正相关。例如,20MB 的 APK 会有 1-2 秒的延迟,我们会利用 Appendix 更好地描述我们的调查结果。
建议:避免调用 ClassLoader.getResource() 方法,而是使用 Android 的 Resources.get(resId) 方法
建议:搜索你的代码看看有没有 SDK 调用了 ClassLoader.getResource*() 方法,有的话把它们全换了,如果你懒的换,就让这些代码在子线程中执行
*现在就去检查你的应用是否因为 ClassLoader.getResource() 方法影响性能!**
我们是怎么在 getResourceAsStream 方法中找到这些操作的?
为了完全理解这个问题,得分析实际的代码。此次分析使用的是 AOSP android-6.0.1_r11 的分支,看的代码是 ClassLoader 类的代码:
libcore/libart/src/main/java/java/lang/ClassLoader.java
public InputStream getResourceAsStream(String resName) {
try {
URL url = getResource(resName);
if (url != null) {
return url.openStream();
}
} catch (IOException ex) {
// Don't want to see the exception.
}
return null;
}```
代码要完成的工作简单直观:先找到资源的路径,如果不为空,就为它打开一个流。在此次分析中,路径是 java.net.URL 类,该类有 openStream() 方法。
现在来检查 getResource() 方法的实现:
```java
public URL getResource(String resName) {
URL resource = parent.getResource(resName);
if (resource == null) {
resource = findResource(resName);
}
return resource;
}```
还是很正常,那继续看 findResource(resName) 方法:
```java
protected URL findResource(String resName) {
return null;
}```
在这里我们发现 findResource(resName) 方法并没有被实现。ClassLoader 是一个抽象类,因此我们需要找到真正实现了相关方法的,在应用中被使用的子类。如果我们去翻阅 Android 文档,我们会看到 Android 提供了几个具体的实现类,而 PathClassLoader 就是通常我们使用的那一个。
既然如此,为了判断到底使用了哪个 ClassLoader,我们就进入 AOSP 看看源码中到底是哪个 ClassLoader 调用了 getResourceAsStream 和 getResource 方法:
```java
public InputStream getResourceAsStream(String resName) {
try {
Logger.getLogger("NimbleDroid RESEARCH").info("this: " + this);
URL url = getResource(resName);
if (url != null) {
return url.openStream();
}
...
}果然,Log 显示的是 dalvik.system.PathClassLoader。然而,检查 PathClassLoader 的方法会发现,并没有
findResource 方法的实现。这是因为 findResource() 方法被 PathClassLoader 类的父类 - BaseDexClassLoader 实现了。
/libcore/dalvik/src/main/java/dalvik/system/BaseDexClassLoader.java:
@Override
protected URL findResource(String name) {
return pathList.findResource(name);
}```
让我们看看 pathList 是啥:
```java
public class BaseDexClassLoader extends ClassLoader {
private final DexPathList pathList;
/**
* Constructs an instance.
*
* @param dexPath the list of jar/apk files containing classes and
* resources, delimited by {@code File.pathSeparator}, which
* defaults to {@code ":"} on Android
* @param optimizedDirectory directory where optimized dex files
* should be written; may be {@code null}
* @param libraryPath the list of directories containing native
* libraries, delimited by {@code File.pathSeparator}; may be
* {@code null}
* @param parent the parent class loader
*/
public BaseDexClassLoader(String dexPath, File optimizedDirectory,
String libraryPath, ClassLoader parent) {
super(parent);
this.pathList = new DexPathList(this, dexPath, libraryPath, optimizedDirectory);
}```
那 DexPathList 是什么呢?
/libcore/dalvik/src/main/java/dalvik/system/DexPathList.java
```java
/**
* A pair of lists of entries, associated with a {@code ClassLoader}.
* One of the lists is a dex/resource path — typically referred
* to as a "class path" — list, and the other names directories
* containing native code libraries. Class path entries may be any of:
* a {@code .jar} or {@code .zip} file containing an optional
* top-level {@code classes.dex} file as well as arbitrary resources,
* or a plain {@code .dex} file (with no possibility of associated
* resources).
*
* <p>This class also contains methods to use these lists to look up
* classes and resources.</p>
*/
/*package*/ final class DexPathList {
Let’s check out DexPathList.findResource:
/**
* Finds the named resource in one of the zip/jar files pointed at
* by this instance. This will find the one in the earliest listed
* path element.
*
* @return a URL to the named resource or {@code null} if the
* resource is not found in any of the zip/jar files
*/
public URL findResource(String name) {
for (Element element : dexElements) {
URL url = element.findResource(name);
if (url != null) {
return url;
}
}
return null;
}```
Element 是 DexPathList 里的一个静态内部类,不妨看看它的代码:
```java
public URL findResource(String name) {
maybeInit();
// We support directories so we can run tests and/or legacy code
// that uses Class.getResource.
if (isDirectory) {
File resourceFile = new File(dir, name);
if (resourceFile.exists()) {
try {
return resourceFile.toURI().toURL();
} catch (MalformedURLException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
}
}
if (zipFile == null || zipFile.getEntry(name) == null) {
/*
* Either this element has no zip/jar file (first
* clause), or the zip/jar file doesn't have an entry
* for the given name (second clause).
*/
return null;
}
try {
/*
* File.toURL() is compliant with RFC 1738 in
* always creating absolute path names. If we
* construct the URL by concatenating strings, we
* might end up with illegal URLs for relative
* names.
*/
return new URL("jar:" + zip.toURL() + "!/" + name);
} catch (MalformedURLException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
}```
我们知道 APK 文件实质上就是 zip 文件,那么:
```java
if (zipFile == null || zipFile.getEntry(name) == null) {
We try to find ZipEntry by a given name. If we do this successfully, we return the corresponding URL. This can be a slow operation, but if we check the implementation of getEntry, we see that it’s just iterating over LinkedHashMap:
/libcore/luni/src/main/java/java/util/zip/ZipFile.java
...
private final LinkedHashMap<String, ZipEntry> entries = new LinkedHashMap<String, ZipEntry>();
...
public ZipEntry getEntry(String entryName) {
checkNotClosed();
if (entryName == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("entryName == null");
}
ZipEntry ze = entries.get(entryName);
if (ze == null) {
ze = entries.get(entryName + "/");
}
return ze;
}```
这并不是特别快的操作,但它也不能耗时过长。
但我们忘了一件事 - 使用 zip 文件前,应该先打开它。回顾 DexPathList.Element.findResource() 方法的实现,你会注意到 maybeInit() 方法的调用,不妨看看它做了什么:
```java
public synchronized void maybeInit() {
if (initialized) {
return;
}
initialized = true;
if (isDirectory || zip == null) {
return;
}
try {
zipFile = new ZipFile(zip);
} catch (IOException ioe) {
/*
* Note: ZipException (a subclass of IOException)
* might get thrown by the ZipFile constructor
* (e.g. if the file isn't actually a zip/jar
* file).
*/
System.logE("Unable to open zip file: " + zip, ioe);
zipFile = null;
}
}```
看到这行代码了么:
```java
zipFile = new ZipFile(zip);```
打开 zip 文件:
```java
public ZipFile(File file) throws ZipException, IOException {
this(file, OPEN_READ);
}```
构造器初始化一个名为 entries 的 LinkedHashMap 对象(为了了解更多有关 Zip 文件的内部结构,不妨看[这里](https://android.googlesource.com/platform/libcore/+/android-6.0.1_r21/luni/src/main/java/java/util/zip/ZipFile.java))。很显然,随 APK 文件体积变大,打开 zip 文件需要的时间也增多。
到现在为止,我们找到了导致 getResourceAsStream 如此慢的第一个原因。如果我们将源码改为下面这样:
```java
public InputStream getResourceAsStream(String resName) {
try {
long start; long end;
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
URL url = getResource(resName);
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
Logger.getLogger("NimbleDroid RESEARCH").info("getResource: " + (end - start));
if (url != null) {
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
InputStream inputStream = url.openStream();
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
Logger.getLogger("NimbleDroid RESEARCH").info("url.openStream: " + (end - start));
return inputStream;
}
...我们就会发现对 zip 文件的操作并不是 getResourceAsStream 方法造成延迟的罪魁祸首:因为 url.openStream() 花费的时间比 getResource() 多多了,不妨继续研究源码:
追踪 url.openStream() 方法的调用栈,会进入 /libcore/luni/src/main/java/libcore/net/url/JarURLConnectionImpl.java
@Override
public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException {
if (closed) {
throw new IllegalStateException("JarURLConnection InputStream has been closed");
}
connect();
if (jarInput != null) {
return jarInput;
}
if (jarEntry == null) {
throw new IOException("Jar entry not specified");
}
return jarInput = new JarURLConnectionInputStream(jarFile
.getInputStream(jarEntry), jarFile);
}```
不妨先看看 connect() 方法
```java
@Override
public void connect() throws IOException {
if (!connected) {
findJarFile(); // ensure the file can be found
findJarEntry(); // ensure the entry, if any, can be found
connected = true;
}
}```
看起来没啥特别的,深入里面的子方法看看吧:
```java
private void findJarFile() throws IOException {
if (getUseCaches()) {
synchronized (jarCache) {
jarFile = jarCache.get(jarFileURL);
}
if (jarFile == null) {
JarFile jar = openJarFile();
synchronized (jarCache) {
jarFile = jarCache.get(jarFileURL);
if (jarFile == null) {
jarCache.put(jarFileURL, jar);
jarFile = jar;
} else {
jar.close();
}
}
}
} else {
jarFile = openJarFile();
}
if (jarFile == null) {
throw new IOException();
}
}```
调用 getUseCaches() 方法应该返回 true,因为:
```java
public abstract class URLConnection {
...
private static boolean defaultUseCaches = true;
...
Let’s look at the openJarFile() method:
private JarFile openJarFile() throws IOException {
if (jarFileURL.getProtocol().equals("file")) {
String decodedFile = UriCodec.decode(jarFileURL.getFile());
return new JarFile(new File(decodedFile), true, ZipFile.OPEN_READ);
} else {
...如你所见,在该方法内我们打开了 Jar 文件,而不是 Zip 文件。然而,JarFile 是 ZipFile 的子类。所以我们找到了影响 getResourceAsStream 方法性能的第二个原因 - Android 需要再次将 APK 文件作为 Zip 文件打开,并索引所有表项。
将 APK 文件作为 Zip 文件打开两次相当于将这部分时间开销加倍,此时对性能的影响就会变得明显了。然而,这部分开销仍然不足以造成 getResourceAsStream 方法的性能总开销,不妨看看 JarFile 的构造方法:
/**
* Create a new {@code JarFile} using the contents of file.
*
* @param file
* the JAR file as {@link File}.
* @param verify
* if this JAR filed is signed whether it must be verified.
* @param mode
* the mode to use, either {@link ZipFile#OPEN_READ OPEN_READ} or
* {@link ZipFile#OPEN_DELETE OPEN_DELETE}.
* @throws IOException
* If the file cannot be read.
*/
public JarFile(File file, boolean verify, int mode) throws IOException {
super(file, mode);
// Step 1: Scan the central directory for meta entries (MANIFEST.mf
// & possibly the signature files) and read them fully.
HashMap<String, byte[]> metaEntries = readMetaEntries(this, verify);
// Step 2: Construct a verifier with the information we have.
// Verification is possible *only* if the JAR file contains a manifest
// *AND* it contains signing related information (signature block
// files and the signature files).
//
// TODO: Is this really the behaviour we want if verify == true ?
// We silently skip verification for files that have no manifest or
// no signatures.
if (verify && metaEntries.containsKey(MANIFEST_NAME) &&
metaEntries.size() > 1) {
// We create the manifest straight away, so that we can create
// the jar verifier as well.
manifest = new Manifest(metaEntries.get(MANIFEST_NAME), true);
verifier = new JarVerifier(getName(), manifest, metaEntries);
} else {
verifier = null;
manifestBytes = metaEntries.get(MANIFEST_NAME);
}
}```
现在我们找到第三个影响性能的操作,所有 APK 文件都被签名,因此 JarFile 会执行验证路径。该验证进程要花费的时间非常长。但这部分的研究已经超出了本文的讨论范围,如果你想了解的话不妨看[这里](https://android.googlesource.com/platform/libcore/+/android-6.0.1_r21/luni/src/main/java/java/util/jar/)。
##总结
总的来说,ClassLoader.getResourceAsStream 之所以慢,是因为这三个操作:
1. 将 APK 文件作为 zip 文件打开,并索引所有 zip 表项
2. 再一次执行 1 的操作
3. 验证 APK 签名是否符合规范
###其他问题
**Q: ClassLoader.getResource*() 在 Dalvik 和 ART 上都很慢吗?**
A: 是的。我们分析了 使用 ART 的 android-6.0.1_r11 和使用 Dalvik 的 android-4.4.4_r2,结果都是一样的。
**Q: 为什么 ClassLoader.findClass() 没有性能的影响?**
A: Android 在安装 APK 时就已经从 APK 文件中解压了 DEX 文件,因此,不需要额外的将 APK 作为 Zip 文件或 Jar 文件打开的操作以找到一个类文件。
如果我们进入 DexPathList 类会看到:
```java
public Class findClass(String name, List<Throwable> suppressed) {
for (Element element : dexElements) {
DexFile dex = element.dexFile;
if (dex != null) {
Class clazz = dex.loadClassBinaryName(name, definingContext, suppressed);
if (clazz != null) {
return clazz;
}
}
}
if (dexElementsSuppressedExceptions != null) {
suppressed.addAll(Arrays.asList(dexElementsSuppressedExceptions));
}
return null;
}```
并没有 Zip 文件或 Jar 文件相关的操作
**Q: 为什么 Android 提供的 Resources.get*(resId) 方法没有这个问题?**
A: Android 拥有自己的索引和加载资源的方式,避免了 Zip 文件和 Jar 文件操作的开销。